2023 Vol. 5, No. 48
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) represents a significant public health challenge globally, not only inflicting harm on the health of individuals but also placing a considerable economic strain on society.
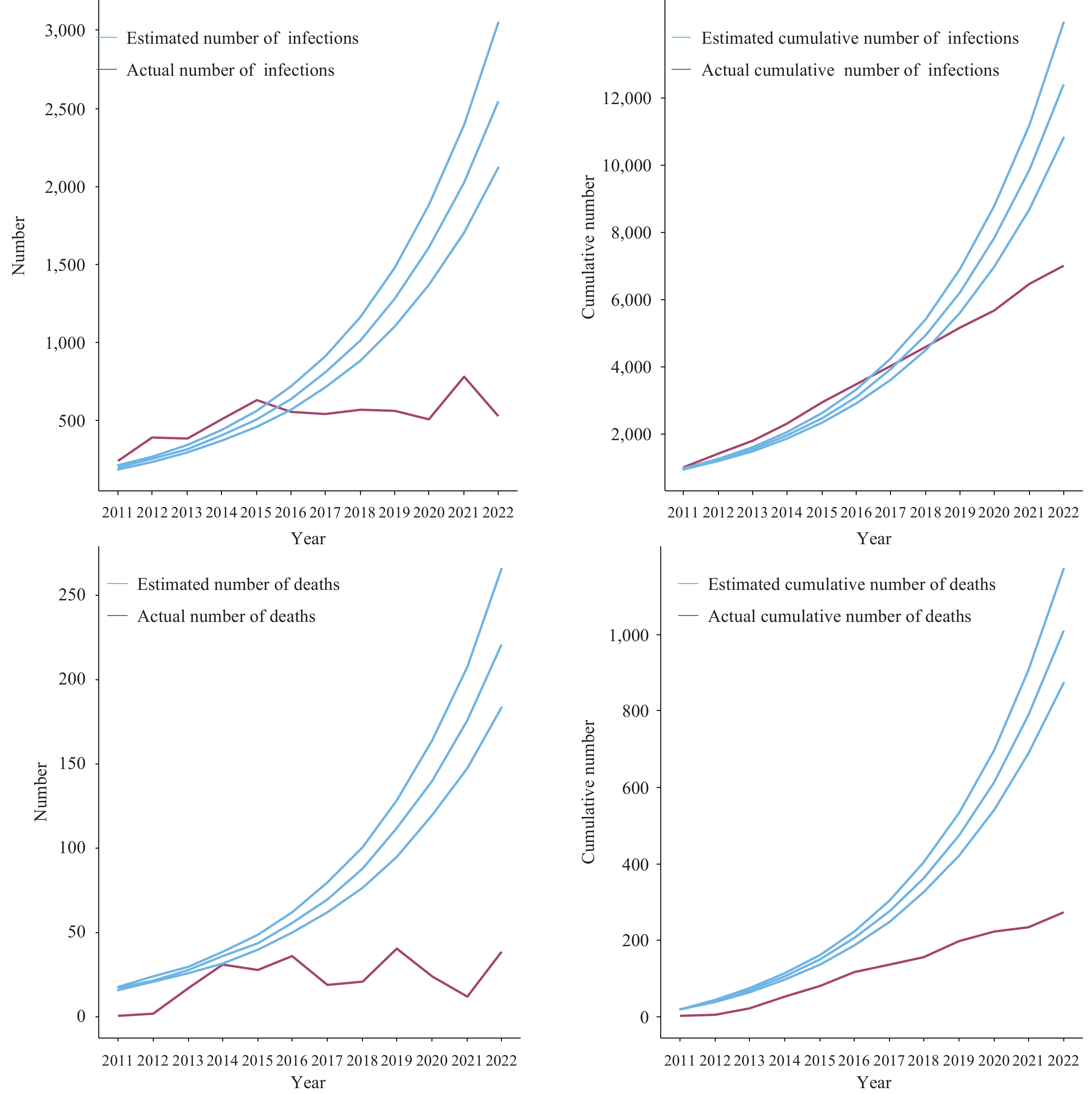
This study represents the inaugural report on the potential reduction in economic burden attributable to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) prevention strategies in Tianjin. Between 2011 and 2022, it is estimated that effective measures could prevent 2,965 new HIV infections and avert 658 deaths, resulting in an economic benefit of approximately 14.437 billion Chinese Yuan.
The findings of this study offer valuable evidence to inform the development of localized HIV prevention and control strategies, as well as to guide public health policymaking.
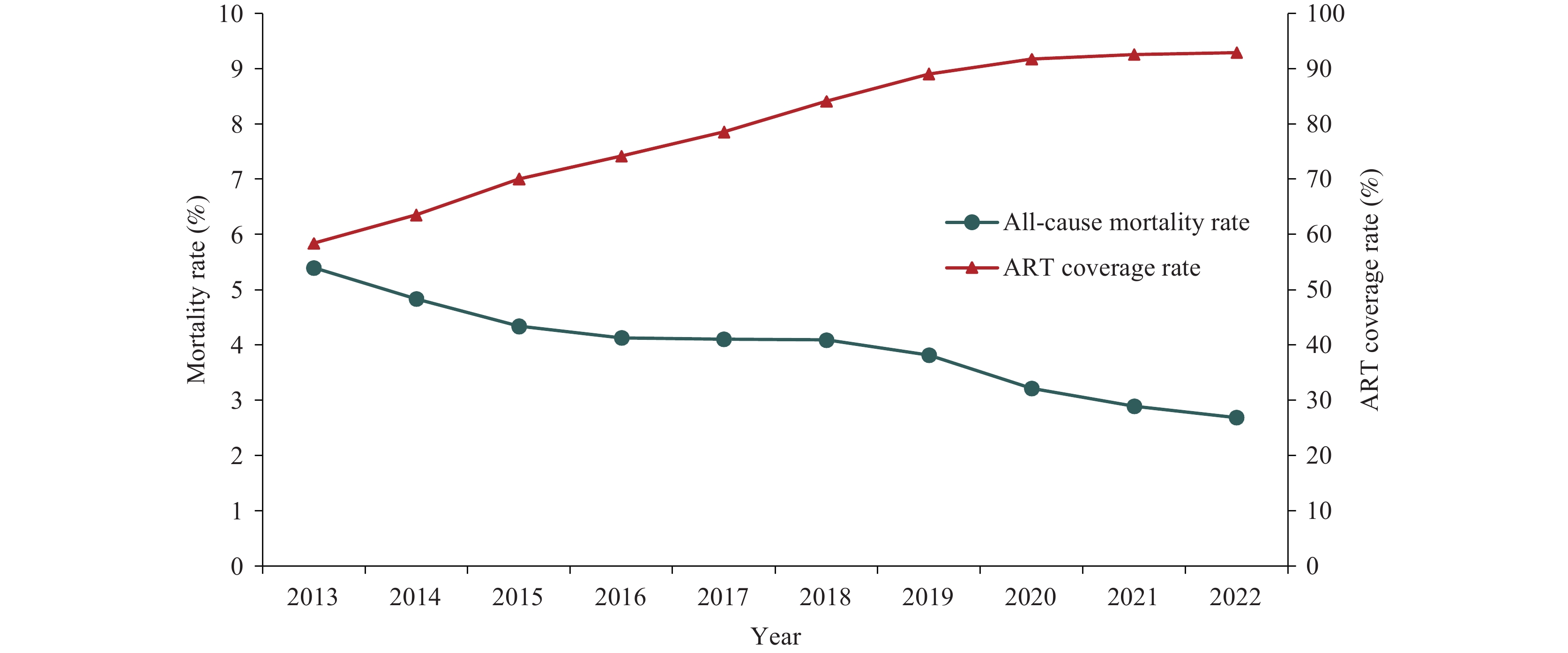
The advent of antiretroviral therapy (ART) has markedly decreased mortality rates among patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Globally, there has been a 43% reduction in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-related deaths from 2010 to 2022. Additionally, prior research indicates that the initiation of ART at an early stage within China has substantially lowered mortality rates.
Over the previous decade, following the implementation of China’s universal ART access strategy, the patterns of mortality causes among HIV-infected individuals across the country have undergone significant alterations. In 2022, the all-cause mortality rate among this population was reported at 2.7%, with the non-AIDS-related mortality rate at 1.8%. However, it is important to consider that the accuracy of death reporting could contribute to potential misclassification of the underlying causes of death.
Efforts to enhance health outcomes should persist in emphasizing the advancement of ART strategies, with a particular focus on mitigating non-AIDS-related mortality in the future.
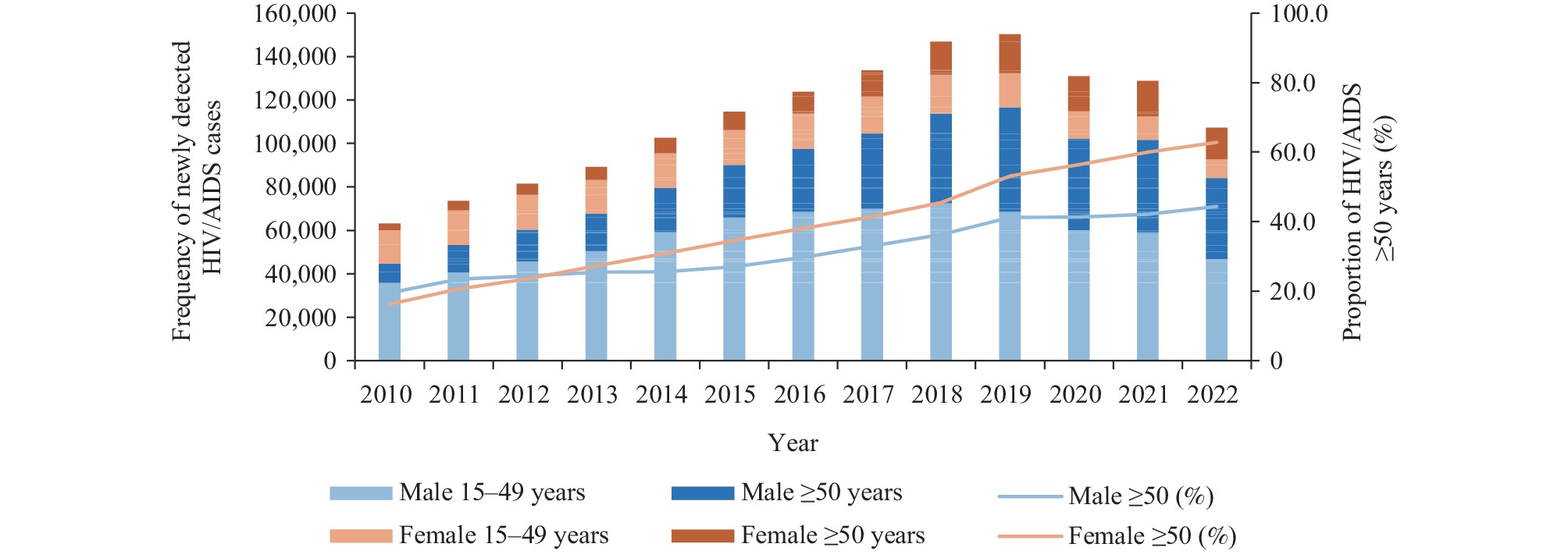
Recent data indicate a year-on-year increase in the proportion of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) cases reported among individuals aged ≥50 in China. This study compares the epidemiological characteristics of HIV/AIDS cases in populations above and below 50 years of age. By doing so, it seeks to scrutinize the current epidemiological landscape of HIV within these distinct age cohorts and suggest tailored interventions for each group.
We utilized data from the Chinese HIV/AIDS Comprehensive Response Information Management System for our comparative analysis. Joinpoint regression analysis was employed to assess the trends in standardized detection rates.
In China, the number of newly reported HIV/AIDS cases in the 15–49 age group increased from 51,436 in 2010 to 55,397 in 2022, while it increased from 11,751 in 2010 to 51,856 in 2022 in the group aged ≥50 years. Recent years have seen a greater proportion and detection rate of HIV/AIDS cases among the ≥50 age demographic compared to the 15–49 age group. In 2022, significant statistical differences were observed between males and females in both age cohorts with respect to education, marital status, occupation, mode of transmission, location of diagnosis, and region.
The observed trend of a rising proportion of HIV/AIDS cases in individuals aged 50 years and older necessitates heightened attention. It is imperative that we develop and implement interventions specifically designed to prevent and control the transmission of HIV within this demographic.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed