2023 Vol. 5, No. 45
The majority of Chinese patients with diabetes failed to achieve the level of physical activity recommended by clinical guidelines.
The prevalence of low-level physical activity was found to be greater in individuals diagnosed with diabetes. It was observed that patients with a protracted duration of diabetes demonstrated a propensity to participate in lower levels of physical activity compared to those with a shorter disease trajectory. The likelihood of engaging in low-level physical activity associated with diabetes was higher in rural inhabitants, those with medium-tier education, employed individuals, and individuals who had longer sleep durations.
Developing strategies and interventions to encourage greater involvement of Chinese diabetic patients in physical activity is essential. However, these strategies must take population characteristics into account.
Current literature underscores the significance of appropriate physical activity in managing diabetes, primarily utilizing self-reported data. Yet, the impact of objectively measured physical activity in older diabetic populations remains unclear.
Our research on elderly diabetic patients indicated a correlation between an increased number of daily steps and improved metabolic profiles, as well as a decrease in the incidence of cardiovascular complications.
Elevated daily step counts may confer significant benefits to elderly individuals with diabetes. The use of devices to monitor these steps could serve as a potent cardiovascular marker, and hold great potential as a screening or intervention tool in community-oriented settings.
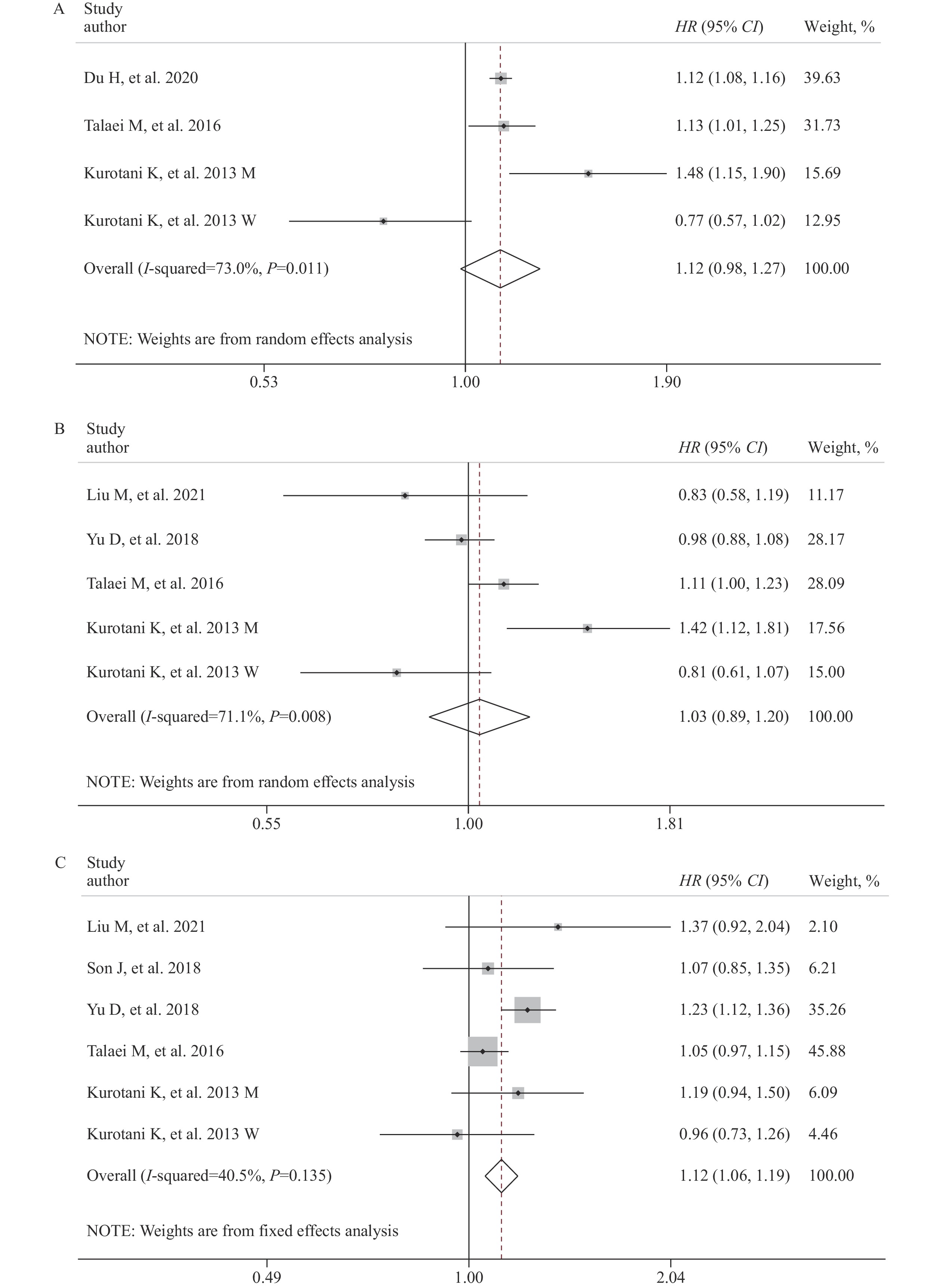
Red and processed meat consumption has been positively related to an increased risk of diabetes in Western populations. However, the results remain inconclusive within Asian populations.
This dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies conducted in East Asian populations reveals a positive relation between the consumption of processed meat and increased risk of diabetes. Furthermore, a U-shaped association was identified between the consumption of unprocessed red meat and the risk of diabetes.
This research presents substantive evidence advocating for the reduction of processed and unprocessed red meat consumption as a viable strategy for mitigating the risk of diabetes in East Asian populations.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed