2023 Vol. 5, No. 44
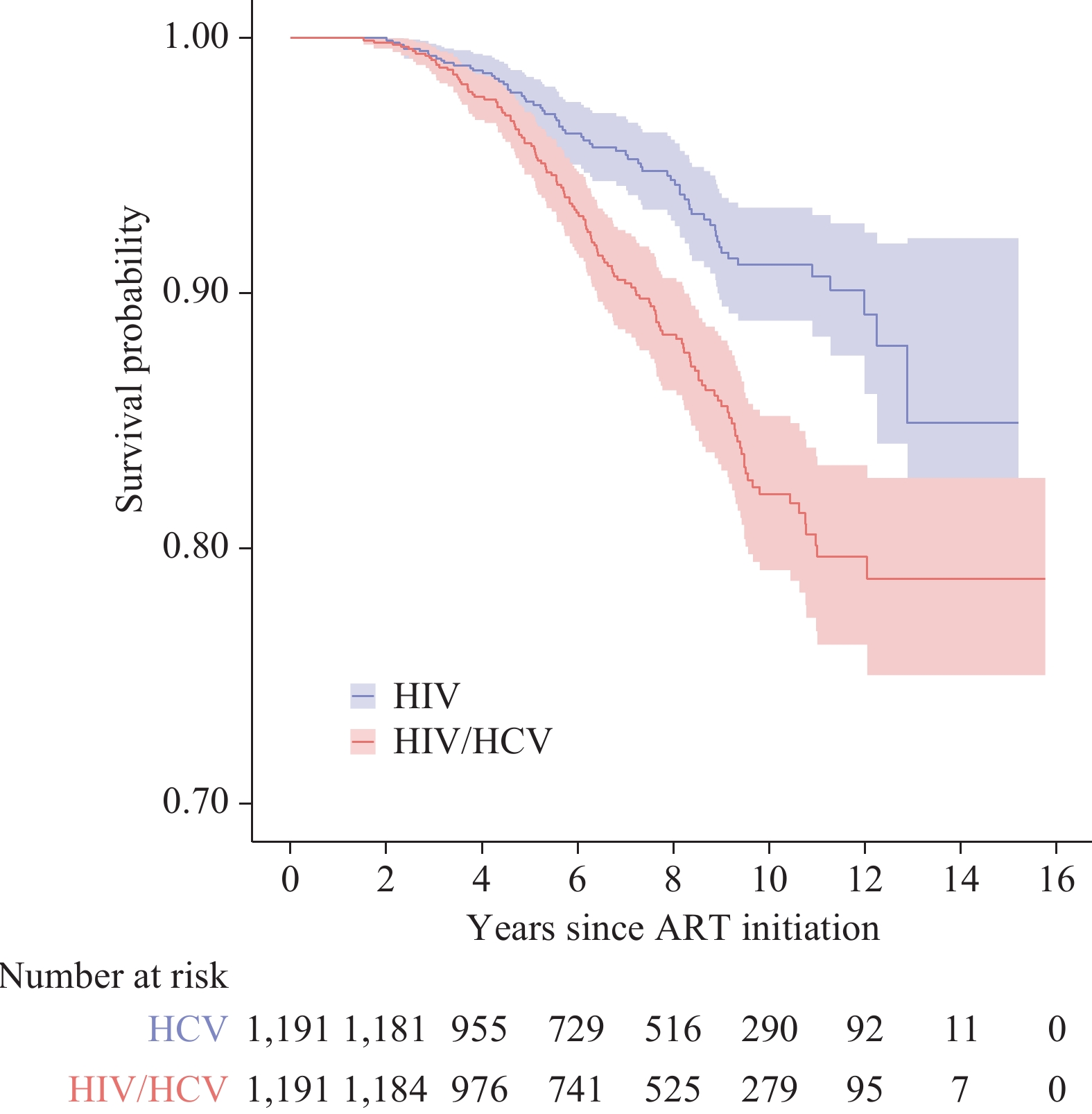
The effects of concurrent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection on mortality and patient attrition in those undergoing antiretroviral therapy continue to be a contested area of research.
According to the propensity score-matched cohort, individuals with HIV/HCV co-infection exhibit an elevated risk of all-cause mortality [adjusted hazard ratio: 2.048, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.526–2.749] and attrition (adjusted incidence rate ratio: 1.659, 95% CI: 1.4.8–1.961) compared to their counterparts who are mono-infected with HIV.
The pressing need for tailored testing and follow-up protocols for individuals co-infected with HIV/HCV cannot be overstated.
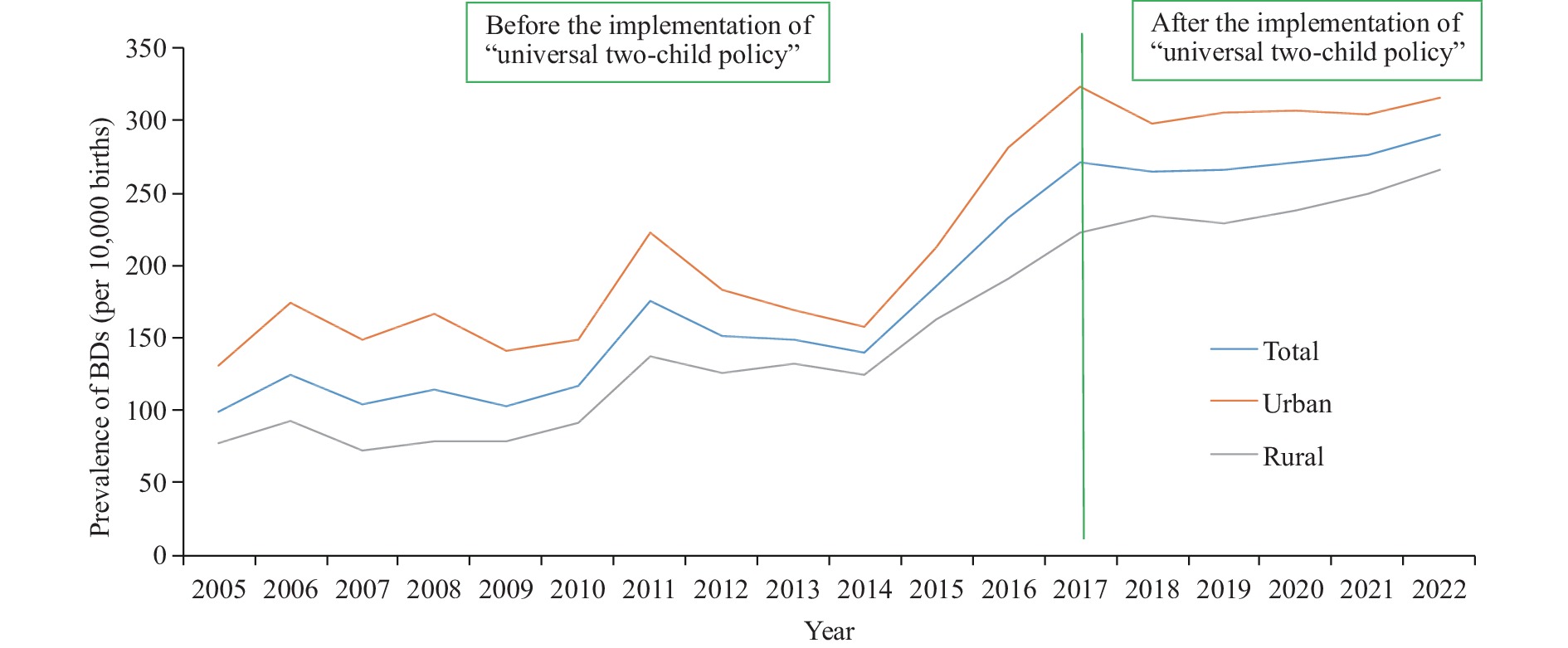
Numerous studies conducted in China have reported on the prevalence of birth defects (BDs). However, the limited surveillance periods in select studies curtail comprehensive trends and cause evaluation. Accordingly, the surveillance duration of BDs is extended, and a comprehensive analysis of their prevailing trends is conducted to provide a basis for government intervention and policy implementation.
There is a distinct increase in the incidence of BDs observed in Jinan. In rural areas, a pronounced upward trend was observed, and the increase was more rapid than in urban areas. BD prevalence among mothers over 35 years old and under 20 years old was substantially higher than BD prevalence rates in other maternal age brackets. Specifically, the period from 2005 to 2022 saw the prevalence of congenital heart disease surge, the fastest average annual growth rate among all birth defects.
It’s essential to prioritize pregnant women in rural areas and those at both ends of the maternal age spectrum. Implementing comprehensive initiatives is crucial to address the high prevalence of congenital heart disease.
Dengue virus (DENV), Chikungunya virus (CHIKV), and Zika virus (ZIKV) are highly pathogenic human arboviruses transmitted by the Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus (Skuse) (Diptera: Culicidae) or Ae. Albopictus mosquito. These arboviruses are responsible for causing fever, hemorrhagic conditions, and neurological diseases in humans post-bite from an infected Aedes mosquito. Over the past 80 years, the Ae. albopictus has infested every habitable continent, bar Antarctica, thereby escalating the probability of global insect-borne infectious disease outbreaks. This research follows the global transmission pattern of Ae. albopictus and provides a summary of disease prevention and control strategies for mosquito-borne infections, as implemented by the World Health Organization (WHO) and both Asian and European countries. Consequently, this study can aid in the prevention and control of mosquito-borne diseases while acting as a basis for international collaboration on effectively managing arbovirus infection issues in public health.
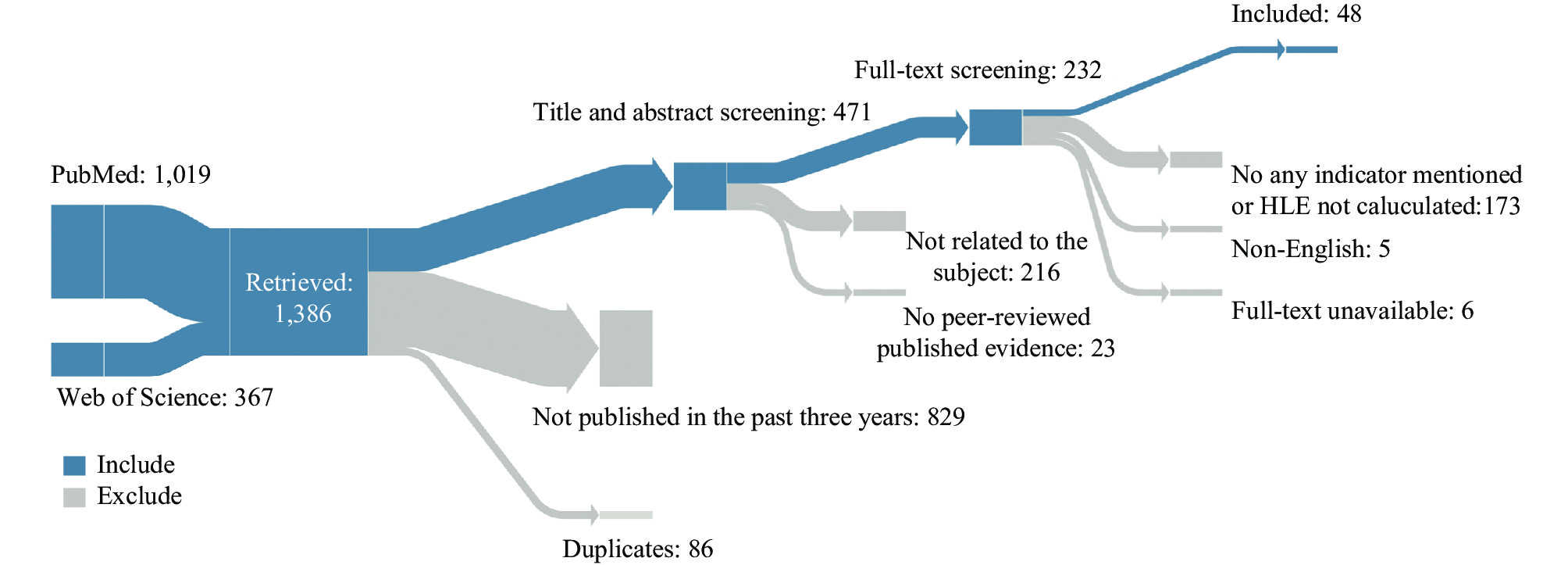
The concept of healthy life expectancy (HLE) integrates the ideas of life expectancy and health status, providing a valuable metric to evaluate both the length and quality of life. This paper seeks to aid policymakers in creating an inclusive HLE indicator system through a systematic review of methodologies for defining and measuring HLE, along with relevant published studies’ descriptions. Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews statement, two English language literature databases were researched from January 2020 to April 2023. Findings from empirical HLE-related studies were analyzed by extracting data on the study area, design, population, healthy state measurement tools, and results of studies using HLE indicators. The current analysis encompassed 48 empirical studies. Researchers discerned 11 unique HLE indicators within this corpus, each concentrating on a particular aspect. Furthermore, the analysis revealed 18 diverse instruments for evaluating health statuses, each varying in its definition of a healthy state, dimensions of measurement, and the categories of data employed. Therefore, merging global health concepts, HLE indicators, methodologies for assessing healthy states, and applied research demonstrations are essential for a consolidated HLE indicator system creation.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed