2023 Vol. 5, No. 43
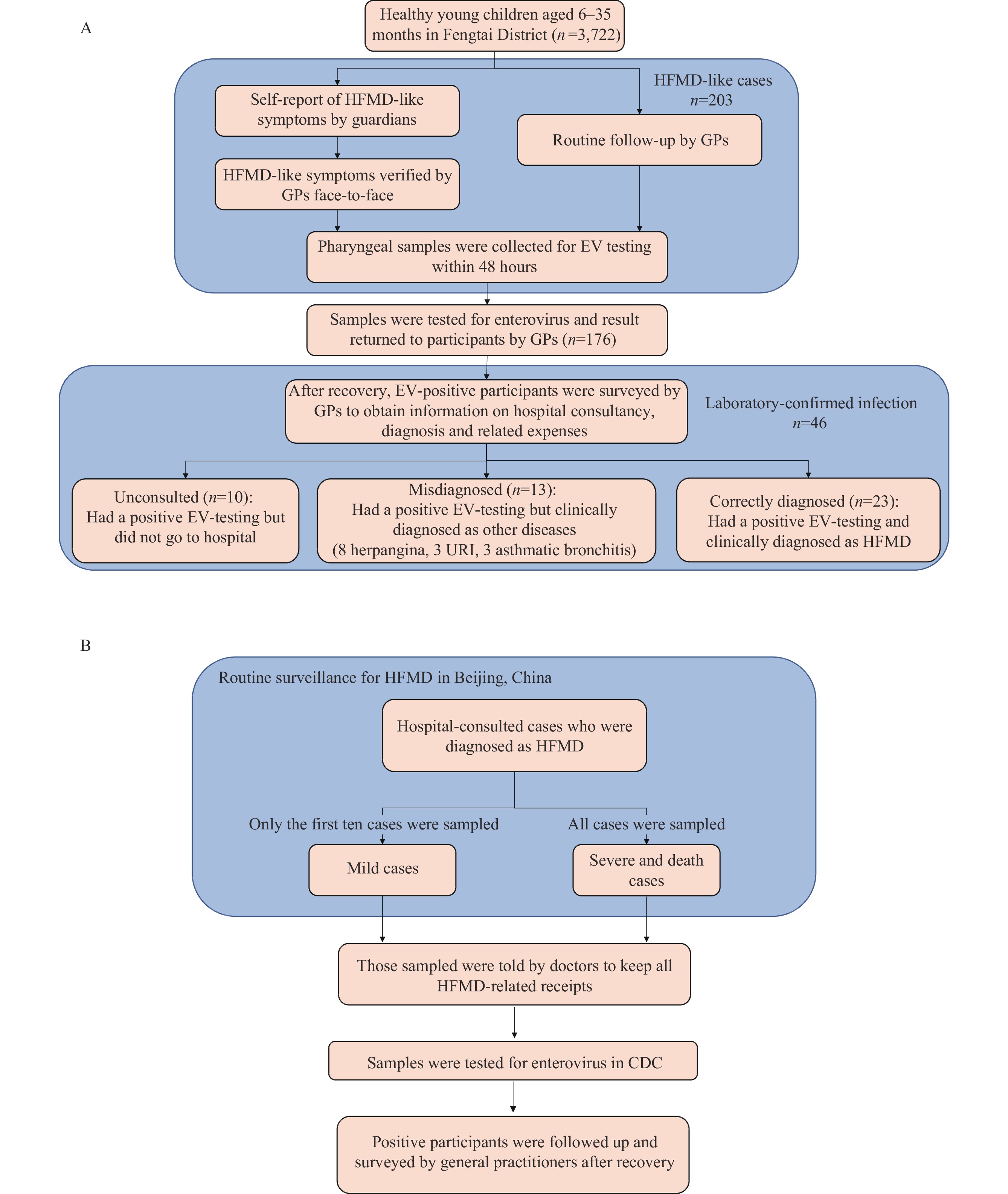
Current research regarding hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) has primarily concentrated on the economic impacts, drawing from retrospective or sentinel hospital-based data. This approach often overlooks cases that were either not consulted or were misdiagnosed.
This research systematically examined the iceberg phenomenon of HFMD and its economic implications in Beijing. Our findings indicate that each confirmed case represents 9.1 actual infections, imposing financial burdens of 25.58 United States dollars (USD) per unconsulted individual, 265.75 USD per misdiagnosed individual, 366.50 USD per individual with mild cases, and 2355.89 USD per individual with severe cases. The annual economic losses attributed to HFMD in the area range from 7.03 million USD to 13.31 million USD.
This study offers insight into the actual prevalence of HFMD in Beijing, as well as conducting an economic burden analysis on a per-case, per-category basis. This could facilitate a cost-effectiveness analysis of prevention and control strategies for HFMD.
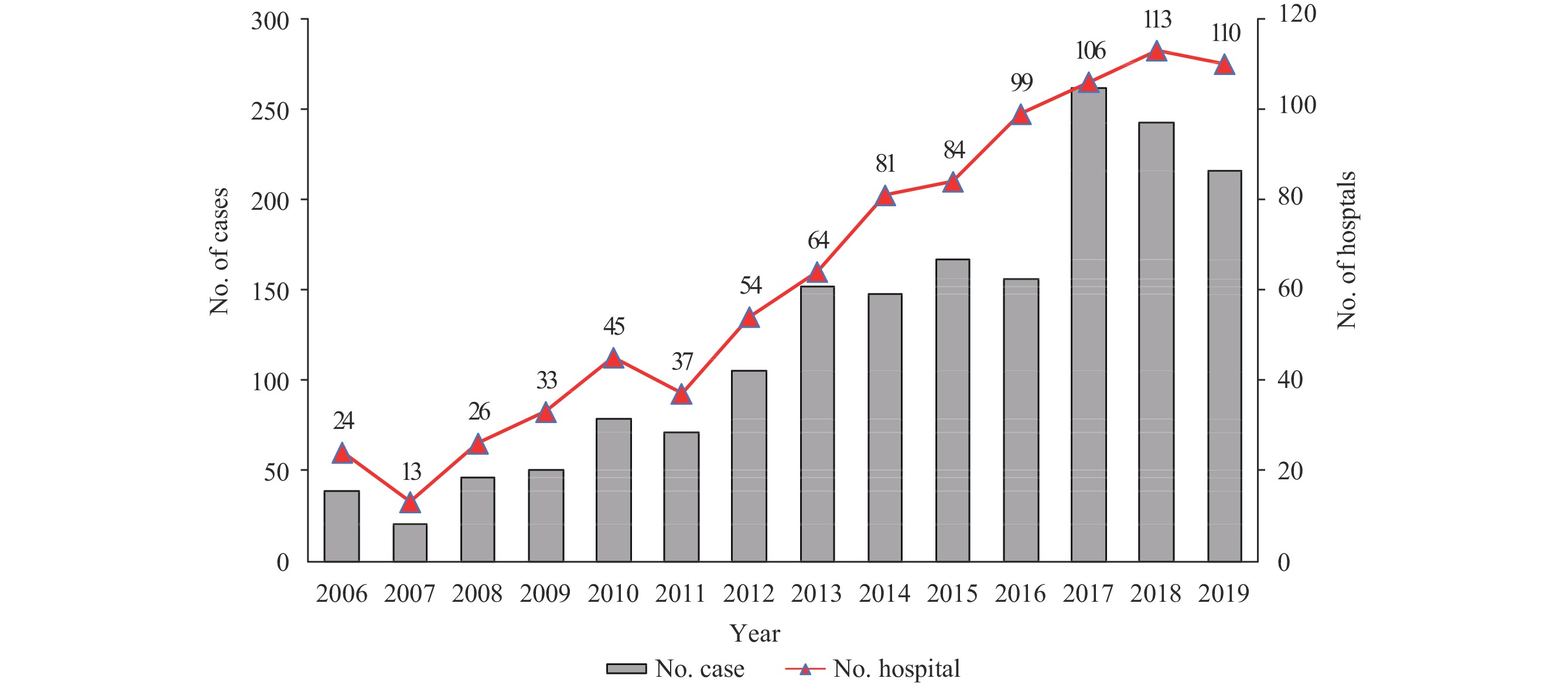
Human prion diseases (PrDs) are rare, fatal encephalopathies requiring comprehensive diagnostic analysis. This study examines hospital referral patterns to the Chinese National Surveillance for Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CNS-CJD) from 2006 to 2019.
We assessed 1,970 PrD cases referred by various hospitals to CNS-CJD. Referral distributions were analyzed based on provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs). Differences in referral numbers and confirmed cases between monitored and non-monitored PLADs were statistically evaluated.
The study included cases from 344 hospitals across 29 Chinese PLADs. Hospital referrals increased over the surveillance years: from 28.2 hospitals annually during 2006–2010, to 64 in 2011–2015, and 107 in 2016–2019. Of these, 12.2% (42/344) of hospitals reported ≥10 PrD cases, accounting for 70.0% (1,379/1,970) of total cases. Referral numbers varied across PLADs, with the top 5 of Beijing (41), Henan (26), Shanghai (21), Guangdong (21), and Jiangsu (21) leading. Additionally, 12 CJD-surveillance PLADs had more referring hospitals and PrD cases than the other 17 non-surveillance PLADs.
Geographical variations in PrD recognition exist across Chinese PLADs, with certain regions and major cities reporting notably higher case numbers.
Dichloromethane (DCM) is a colorless and transparent organic solvent that commonly causes poisoning during occupational contact.
Unknown to teachers and students, they were utilizing an acrylic paint cleaner that contained DCM. At the time of the poisoning incident, the art room was occupied beyond its capacity with inadequate local ventilation. The primary cause of the incident was determined to be the students’ inhalation of DCM during the cleaning process.
The unclear composition of environmental cleaning products available for purchase online presents a major obstacle for consumers trying to assess their toxicity. It is imperative that robust regulatory measures and proactive public education campaigns are implemented to mitigate instances of poisoning.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed