2023 Vol. 5, No. 42
Viral hepatitis continues to present a major global public health challenge, with China shouldering the heaviest burden of this disease worldwide.
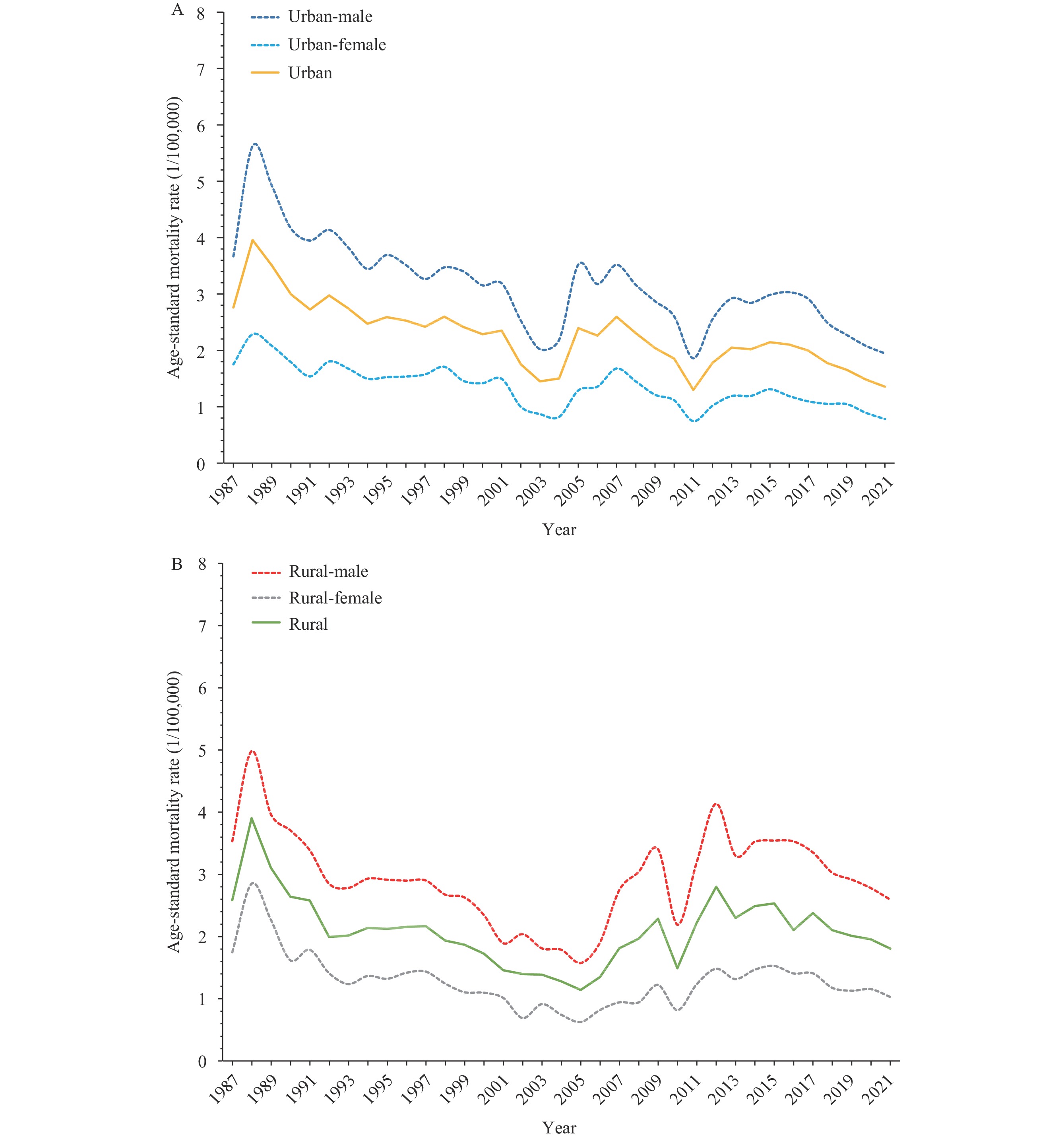
This study examined evolving trends and assessed the impacts of age, period, and cohort on viral hepatitis mortality from 1987 to 2021 in both urban and rural settings across China.
This research provides critical insights, enabling policymakers to develop precise and effective intervention strategies that are specifically tailored to address the needs of high-risk older adults.
In China, an estimated 780,000 individuals contract tuberculosis (TB) every year. With TB ranked as the second most prevalent disease in terms of the morbidity and mortality rates for legally infectious diseases, it imparts a substantial disease burden on families and society.
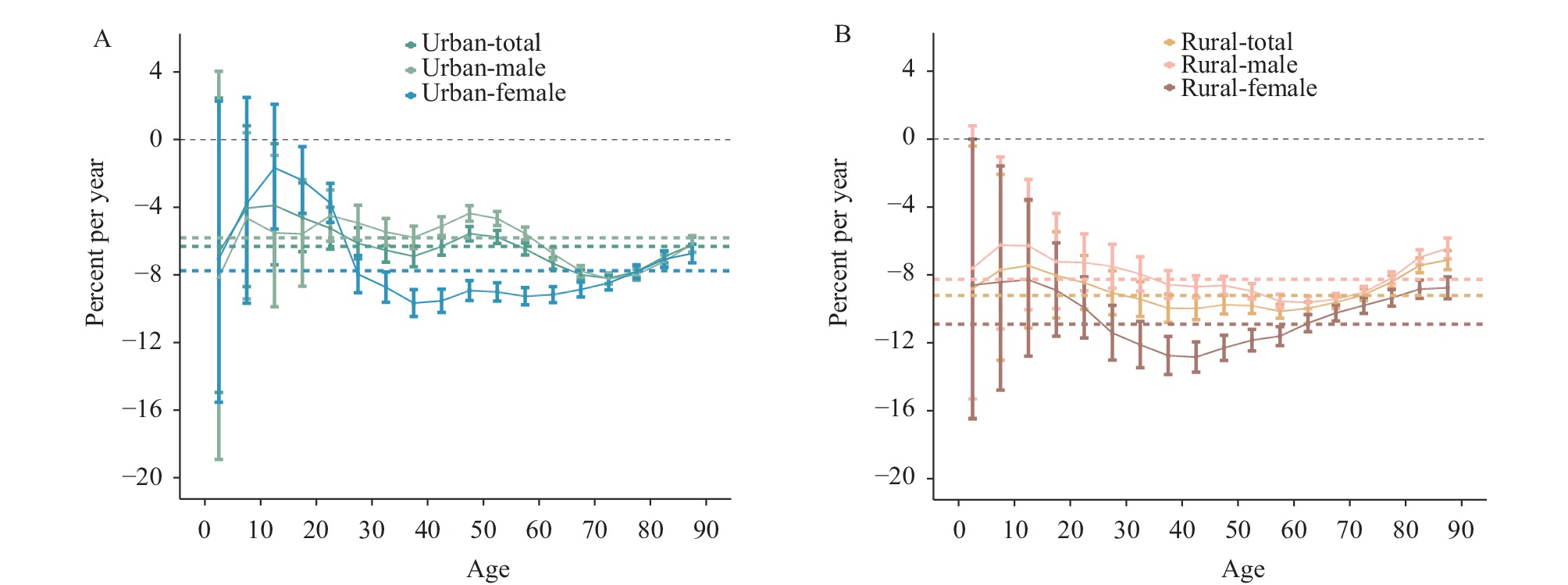
This study identifies specific periods and cohort effects related to trends in respiratory TB mortality in both rural and urban regions of China. The mortality rates have been found to decrease at an annual rate of 5.5% in urban regions and 6.6% in rural ones, with a more marked decline evident in rural areas. These findings represent a significant milestone in the prevention and treatment of respiratory TB in China, especially in its rural locales.
This research contributes to policymakers’ comprehension, assisting in the early formulation of cogent optimization policies, thereby further supporting the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Endeavor to End Respiratory TB Strategy. It is recommended that policymakers prioritize key groups such as children, young adults aged 20–30 in rural areas, and older men (60 years and over) in urban areas when developing these astute optimization policies.
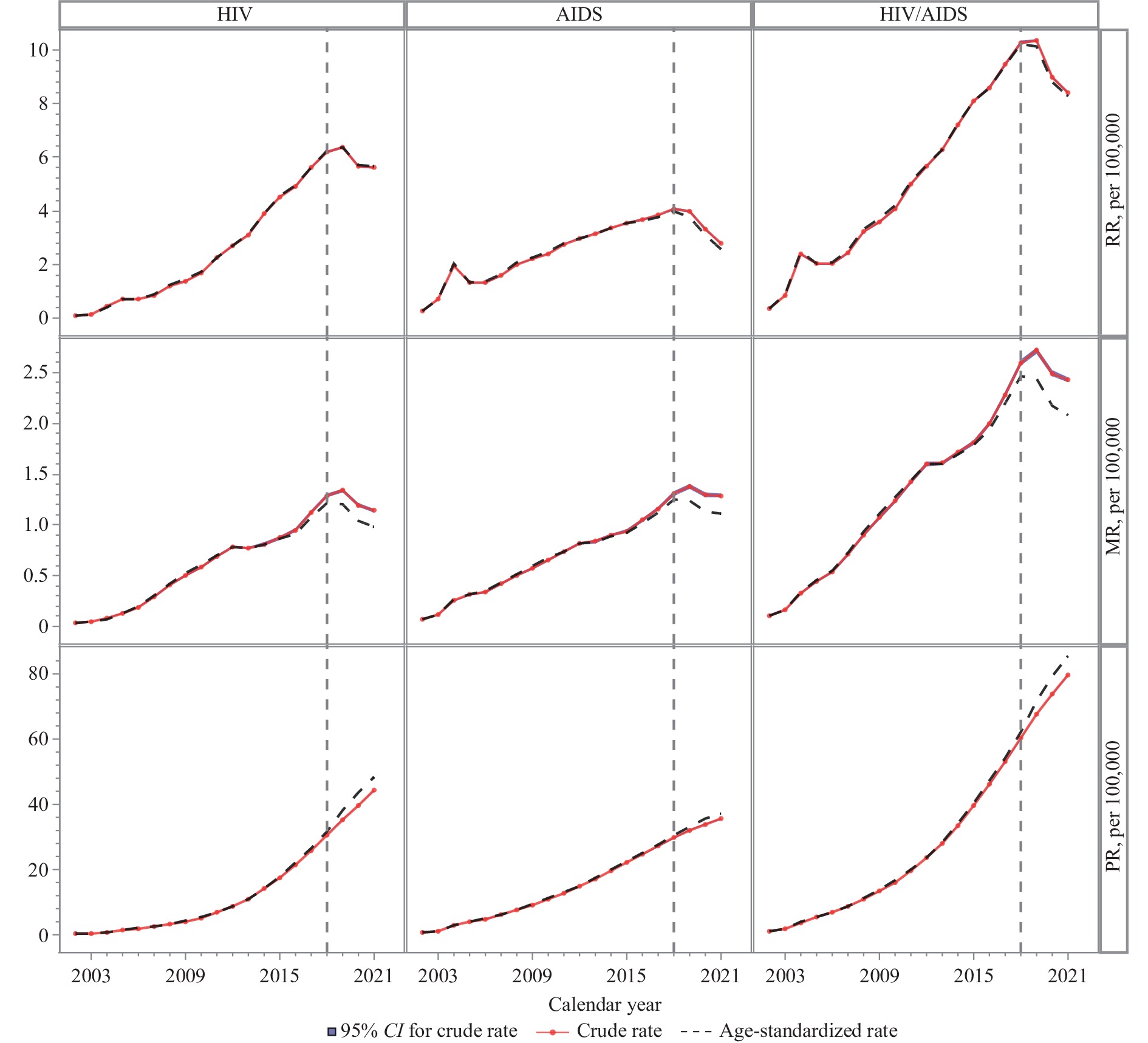
Annually, only the incidence and mortality for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) patients are officially disclosed.
For the first time, information detailing the reported rate, mortality rate, and prevalence rate trends of HIV, AIDS, and HIV/AIDS in China’s entire population over the past two decades has been provided.
Our research overcomes the longstanding limitation of HIV/AIDS analysis as the sole denominator. Rather, it incorporates a comprehensive examination of the overall population, utilizing indicators and analytic methods from chronic disease analyses.
In recent decades, China has experienced significant alterations in its landscape of infectious diseases, with noteworthy reductions in historically prevalent illnesses such as tuberculosis and viral hepatitis. At the same time, emerging pathogens like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Influenza A virus subtype H7N9 (H7N9), and SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pose new challenges. These epidemiological shifts, fueled by fast economic development, urbanization, modifications in the healthcare system, and an aging population, present considerable obstacles to the country’s public health infrastructure and policy frameworks. This article provides a comprehensive review of these changes, underscoring the driving forces behind them and the resultant impact on health policy and infrastructure. It stresses the challenges and calls for an intensification of surveillance efforts, the establishment of collaborative partnerships both nationally and internationally, the encouragement of worldwide cooperation, and the reinforcement of public health education as pivotal strategies for managing China’s changing spectrum of infectious diseases.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed