2023 Vol. 5, No. 39
Previous research has identified a link between economic deprivation, internet usage, and subjective relative deprivation in the general populace. However, few studies have explored the mediating role of internet usage in the relationship between economic deprivation and subjective relative deprivation, particularly in relation to middle-aged and older adults with disabilities.
This research examines the circumstances of middle-aged and older Chinese adults living with disabilities, using the most recent data available. The study uncovers both absolute and relative economic deprivation as key factors significantly correlated with subjective relative deprivation. Additionally, it emphasizes the mediating role of internet usage within this specific relationship.
The connection between subjective relative deprivation and adverse physical and mental health outcomes has been firmly established, which underscores the critical need to address economic deprivation and enhance internet accessibility. Implementing such strategies is essential for mitigating the effects of subjective relative deprivation within this particular demographic.
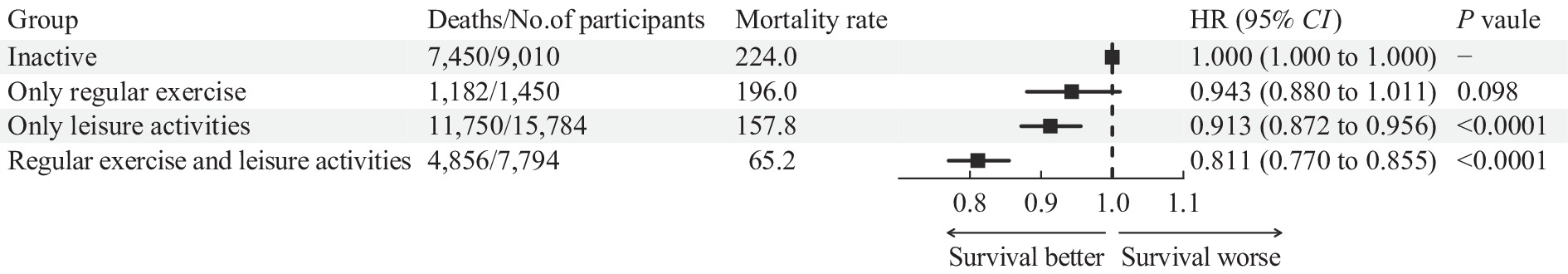
Previous research indicates that non-occupational physical activity can reduce mortality risk. Nevertheless, the relationship between occupational physical activity and health improvements has not been consistently established.
The study found that regular exercise and leisure activities reduced the risk of all-cause mortality. However, the combination of exercise and leisure activities demonstrated more substantial benefits. Additionally, no meaningful association was identified between physical work and mortality risk within the older population.
It may be beneficial to encourage older adults to engage in regular exercise and to partake actively in leisure activities. Combining these two elements might yield greater benefits than regular exercise alone.
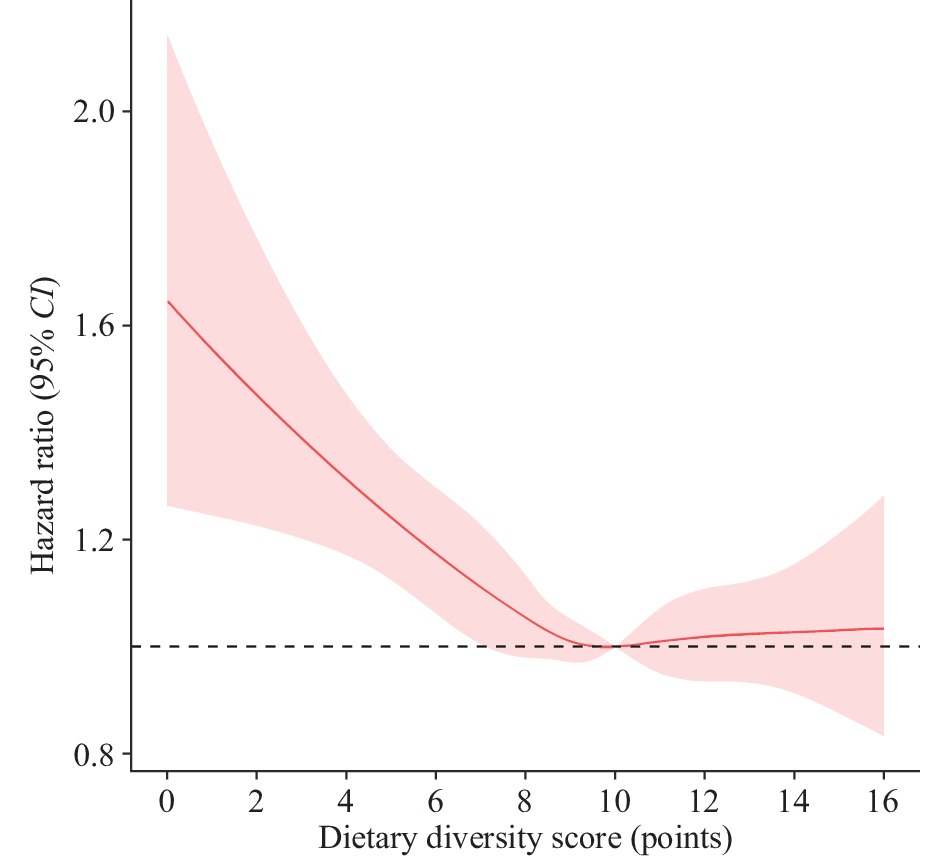
The relationship between specific dietary patterns and dietary diversity with cognitive frailty continues to be a subject of ambiguity.
This research revealed that regular consumption of fruit, meat, bean products, garlic, and tea was connected to a decreased risk of cognitive frailty. Compared to participants with dietary diversity score (DDS) ≤6 points, those with DDS of 9–10, 11–12, and ≥12 had a lower risk of cognitive frailty.
The results of the study corroborate the relationship between the augmented consumption frequency of meat, fruit, bean products, garlic, and tea, in conjunction with an elevated DDS, and an increased risk of developing cognitive frailty.
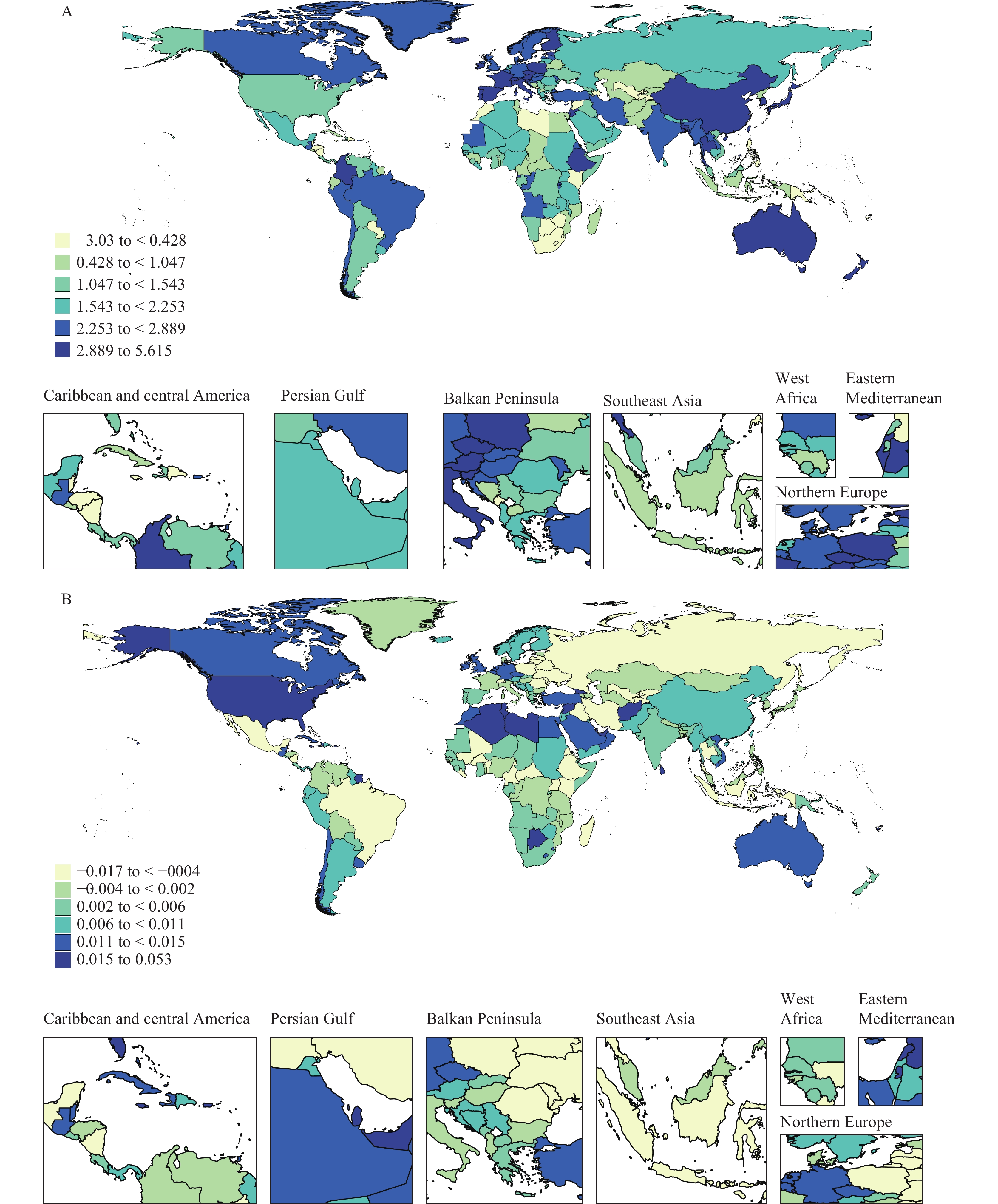
Traditionally, life expectancy has served as a pivotal measure for assessing population health. However, there is an increasing focus on distinguishing healthy years of life from those characterized by illness, particularly among the elderly population.
This study conducts an exhaustive global analysis of the trends in healthy and unhealthy life expectancy among adults aged 60 and over from 1990 to 2019. These trends are further correlated with socio-demographic indicators and health services metrics.
Comprehending the dynamics between healthy and unhealthy life years can equip policymakers with the necessary insights to prioritize interventions. These interventions can thereby secure both quality and longevity of life for the increasingly aging population.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed