2023 Vol. 5, No. 38
Pneumoconiosis, recognized as one of the most detrimental occupational diseases in China, exhibits a multimorbidity profile due to a plethora of comorbidities and complications. These factors significantly influence the treatment outcomes, progression, prognosis, and overall quality of life of the afflicted patients.
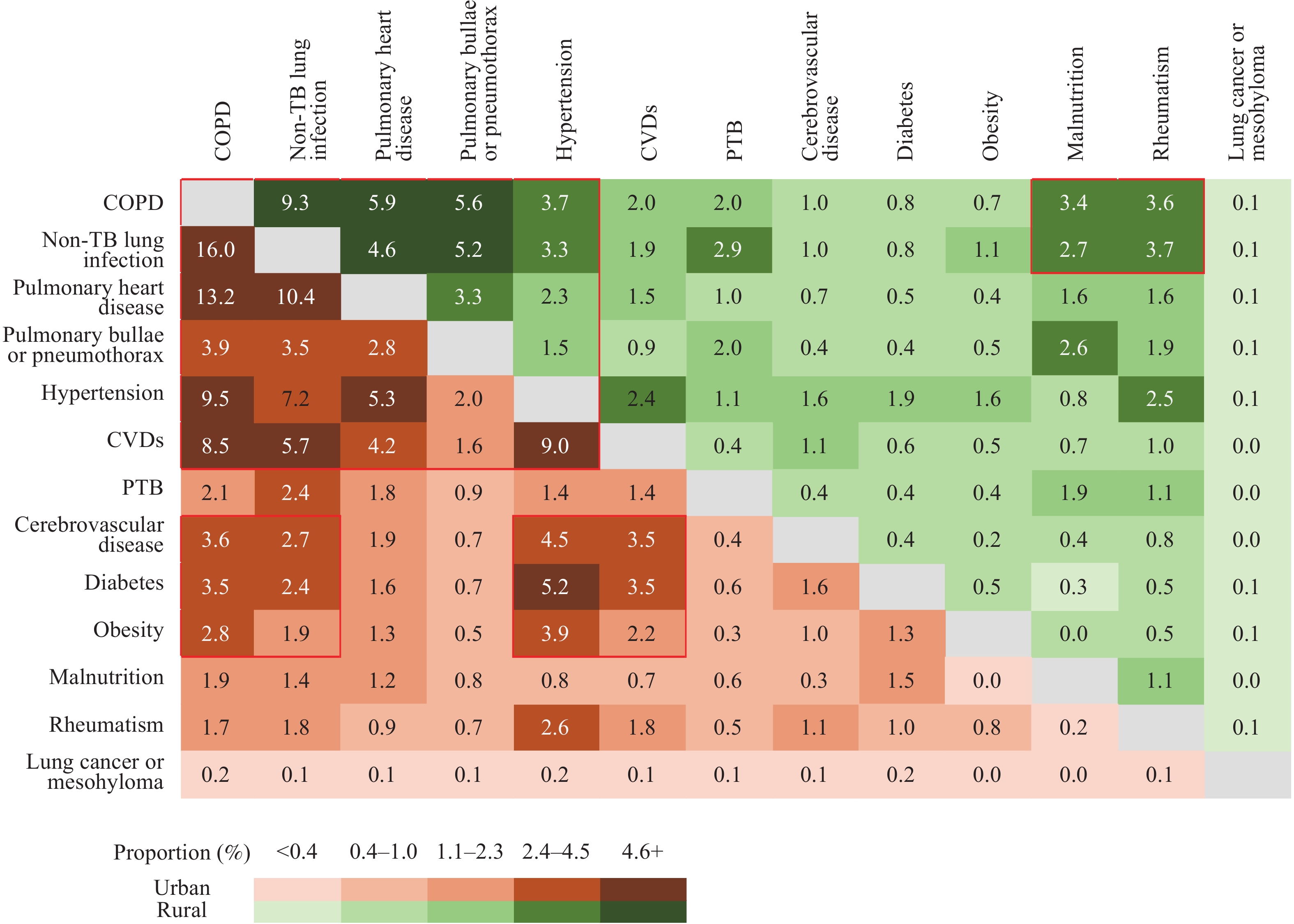
The present study examined the prevalence and types of comorbidities, encompassing 13 common diseases or conditions, within cases of pneumoconiosis across 27 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) in China. Distinctions in multimorbidity distribution by gender, urban vs. rural areas, stages of pneumoconiosis, and the smoking index were considered. Furthermore, the study investigated the patterns of multimorbidity.
This study serves as a reference point for the formulation of treatment strategies and health policy development concerning pneumoconiosis in China.
The application of whole lung lavage (WLL) for the clinical treatment of pneumoconiosis is prevalent in China. Several scholars have reported success in the treatment of early-stage pneumoconiosis. Nonetheless, the overall efficacy of WLL in the management of pneumoconiosis remains ambiguous.
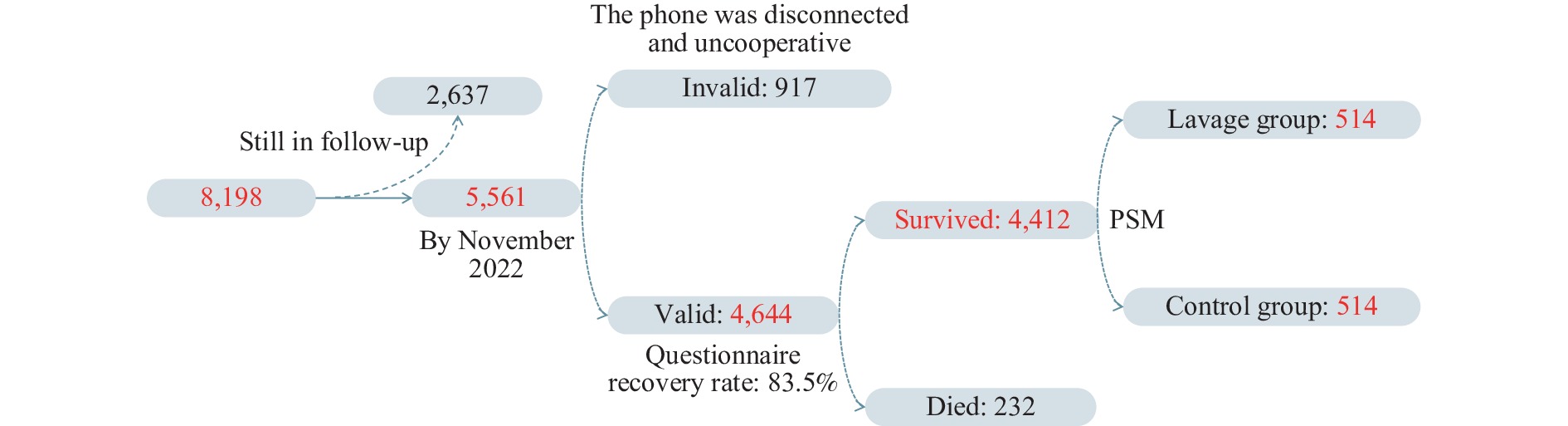
The preliminary evaluation of the effects of WLL on pneumoconiosis patients was conducted using follow-up data from 2020 to 2022, after controlling for confounding factors via propensity score matching. While the study found that WLL may improve some pneumoconiosis symptoms, no significant enhancements were observed in overall health status or quality of life.
The findings of this research indicate limited efficacy of WLL in treating patients with pneumoconiosis, thereby suggesting that it should not be utilized as a standard treatment procedure for this condition.
Pneumoconiosis emerges as the most critical and prevalent occupational disease in China at present, according to research. Studies indicate that pneumoconiosis may indeed impact the body’s phospholipid metabolism.
In this study, serum samples were taken from 46 paired participants, which included patients with pneumoconiosis and dust-exposed workers. We employed ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) technology in targeted lipidomics to investigate serum target phospholipids. Initially, a pilot study was conducted with a selection of 24 pneumoconiosis patients and 24 dust-exposed workers, using both univariate and multivariate statistical analyses to preliminarily identify significant differences in phospholipids. Subsequent to this, the remaining subjects were engaged in a validation study, wherein receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to further substantiate the screening potency of potential lipid biomarkers for pneumoconiosis.
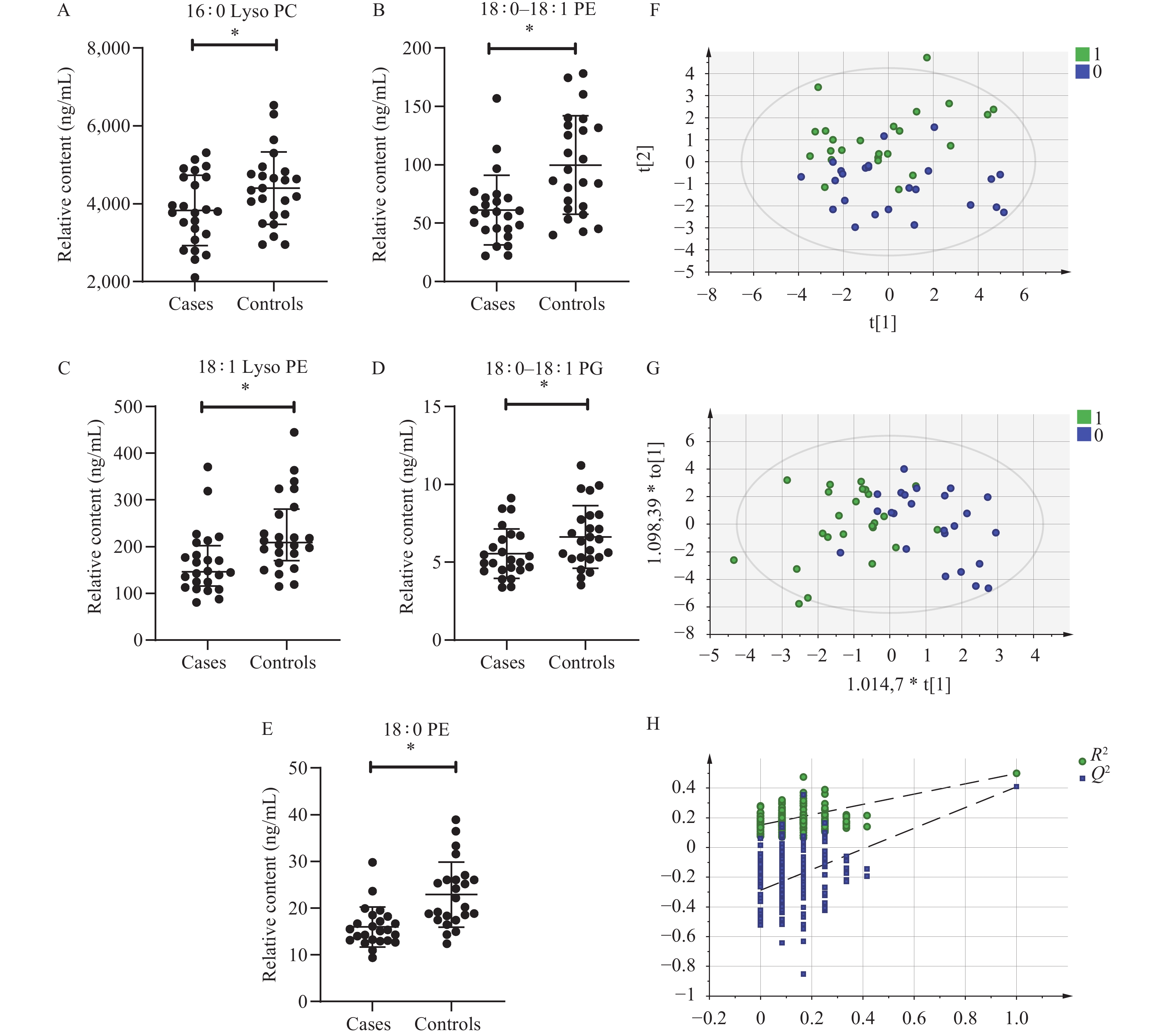
The pilot study revealed significantly reduced serum levels of 16∶0 lysophosphatidylcholines (Lyso PC), 18∶0–18∶1 phosphatidylglycerol (PG), 18∶0–18∶1 phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), 18∶0 PE, and 18∶1 lysophosphatidylethanolamine(Lyso PE) in the case group in comparison to the control group. Additionally, 18∶0 PE, 18∶0–18∶1 PE, and 18∶1 Lyso PE emerged as significant phospholipids with superior diagnostic values [area under the curve (AUC)>0.7]. A diagnostic model was established, built on 16∶0 PC and 18∶0 PE (AUC>0.8). In the ROC analyses of validation studies, the 18∶0–18∶1 PE and this diagnostic model demonstrated excellent screening efficiency (AUC>0.7).
A significant divergence in phospholipid metabolism has been observed between pneumoconiosis patients and dust-exposed workers. The 18∶0–18∶1 PE present in serum could potentially function as a lipid biomarker for pneumoconiosis. Additionally, diagnostic models were developed relying on 16∶0 PC and 18∶0 PE, proving to have superior screening efficiency.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed