2023 Vol. 5, No. 28
Research on community-based smoking cessation interventions in China is still in its early stages. Most existing studies have focused on a limited number of communities and have primarily examined interventions conducted by study teams rather than broader community initiatives.
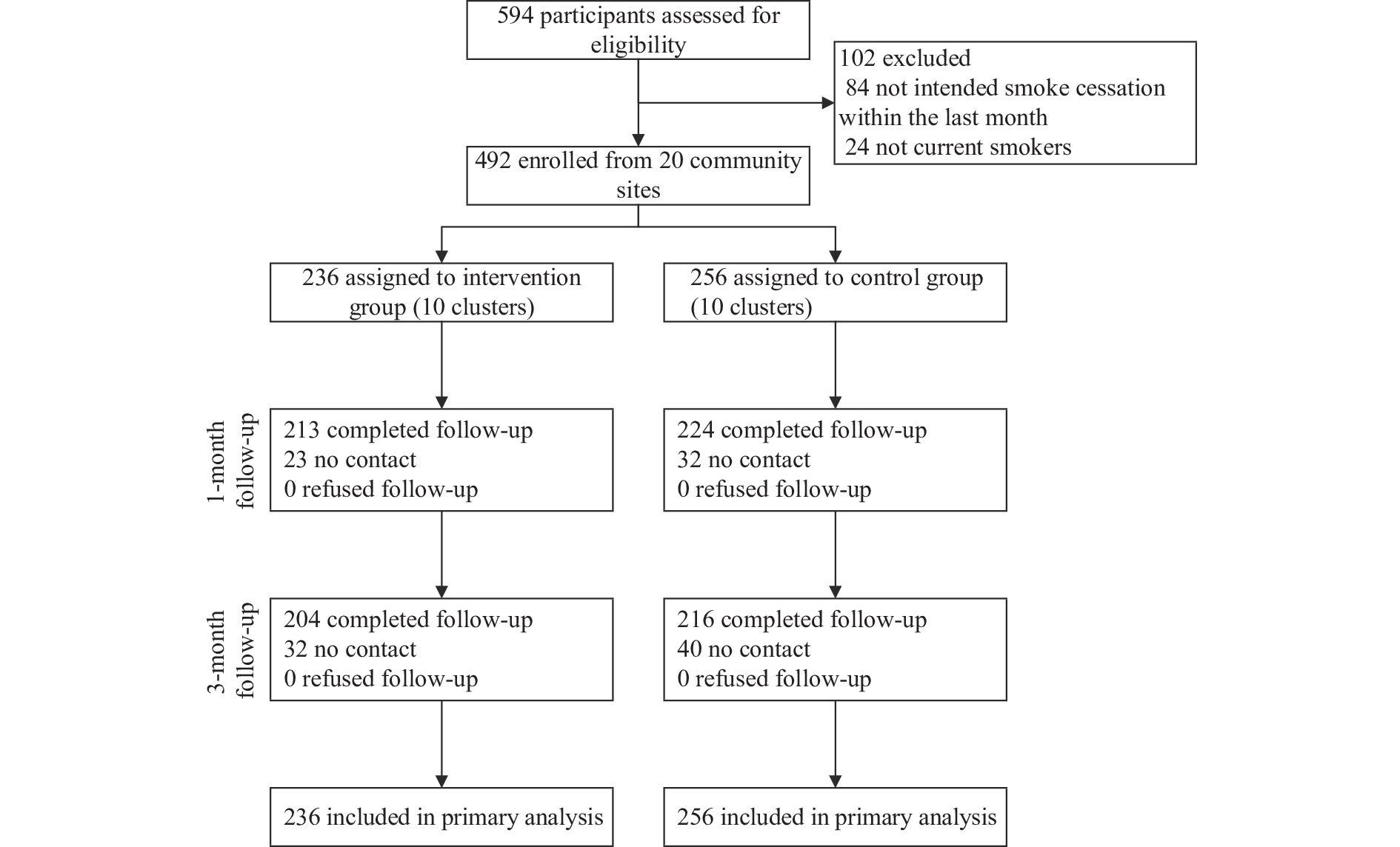
The three-month continuous abstinence rate for the intervention group (21.61%) was significantly higher than that for the control group (8.98%). Comprehensive community-based smoking cessation interventions, administered by trained physicians at community health service centers and supported by community workers, have shown effectiveness in improving a variety of outcomes among community smokers.
The feasibility and effectiveness of comprehensive community-based smoking cessation interventions make them a valuable addition to existing cessation services in China. Wider implementation of these interventions should be pursued as a complementary approach to current efforts to reduce smoking rates in China.
Human sapovirus (HuSaV) is an enteric virus responsible for sporadic cases and outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis (AGE) globally. A seven-year active surveillance study was conducted to investigate the molecular epidemiology of HuSaVs associated with AGE outbreaks in Chaoyang District of Beijing Municipality, China from January 2015 to December 2021.
Fecal and anal swab samples were obtained from patients experiencing AGE outbreaks. HuSaVs were identified through reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and partial viral protein 1 (VP1) sequences (approximately 434 base pairs) were utilized for genotyping, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis, and phylogenetic examination.
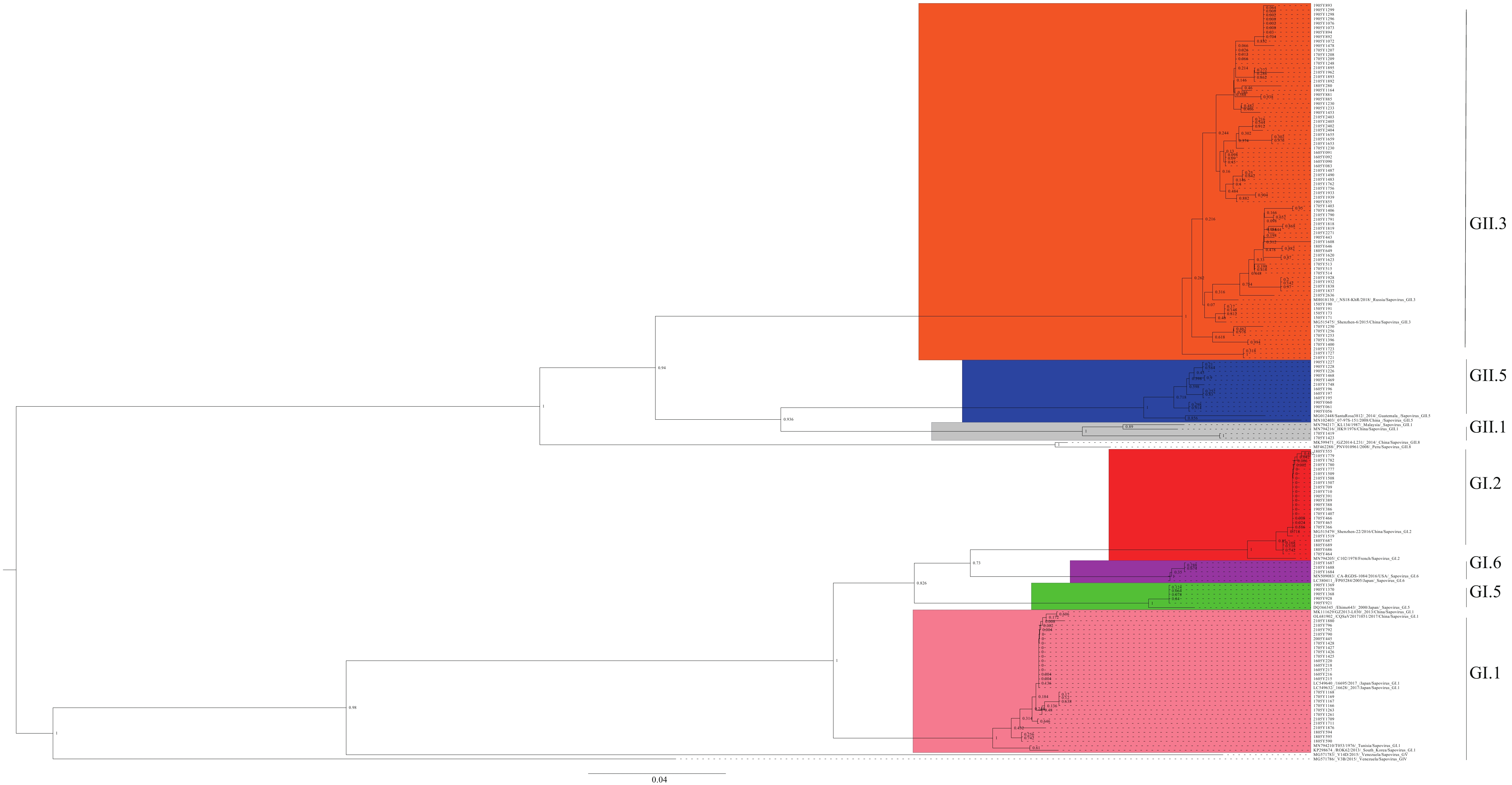
HuSaVs were identified in 71 AGE outbreaks, demonstrating a detection rate of 10.5%, second only to norovirus. The primary demographic affected by HuSaV were children under the age of 5 in kindergarten settings. Infection rates tended to peak during two distinct periods: May to June and September to December. Upon genotyping, seven distinct genotypes emerged. GII.3 was the most prevalent, accounting for 54.9% of cases, followed by GI.1 (12.7%), GI.2 (9.9%), GII.5 (7.0%), GI.5 (2.8%), GI.6 (1.4%), GII.1 (1.4%), and untyped cases (9.9%). A phylogenetic analysis of GII.3 identified three distinct groups, with 15 notable SNPs observed.
This study offers a comprehensive analysis of the persistent prevalence of HuSaV outbreaks in Chaoyang District, Beijing Municipality, China. Over time, the diversity of HuSaV subtypes has shifted, and it is now recognized as the second leading viral agent responsible for AGE outbreaks. This highlights the importance of ongoing surveillance in the future.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed