2023 Vol. 5, No. 2
Limited evidence on healthy longevity was provided in the world, and no studies investigated the fractions of healthy longevity attributed to modifiable factors.
Incidences of longevity and healthy longevity in China are provided. It reveals that the total weighted population attributable fractions for lifestyles and all modifiable factors were 32.8% and 83.7% for longevity, respectively, and 30.4% and 73.4% for healthy longevity, respectively.
China has a high potential for longevity and healthy longevity. Strategies may be targeted at education and residence in early life as well as healthy lifestyles, disease prevention, and functional optimization in late life.
Dyslipidemia is attributed to cardiovascular disease (CVD). A recent report suggests dyslipidemia prevalence has increased among children and adolescents.
Dyslipidemia prevalence was 19.43% among Chinese children and adolescents aged 6–17 years in 2016–2017. The abnormal blood lipid prevalence and the average blood lipid levels showed a diversified distribution across demographics.
Continued monitoring of abnormal blood lipids among Chinese children and adolescents, especially triglyceride (TG) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), may inform public health interventions to promote long-term cardiovascular health and prevent CVD in adulthood.
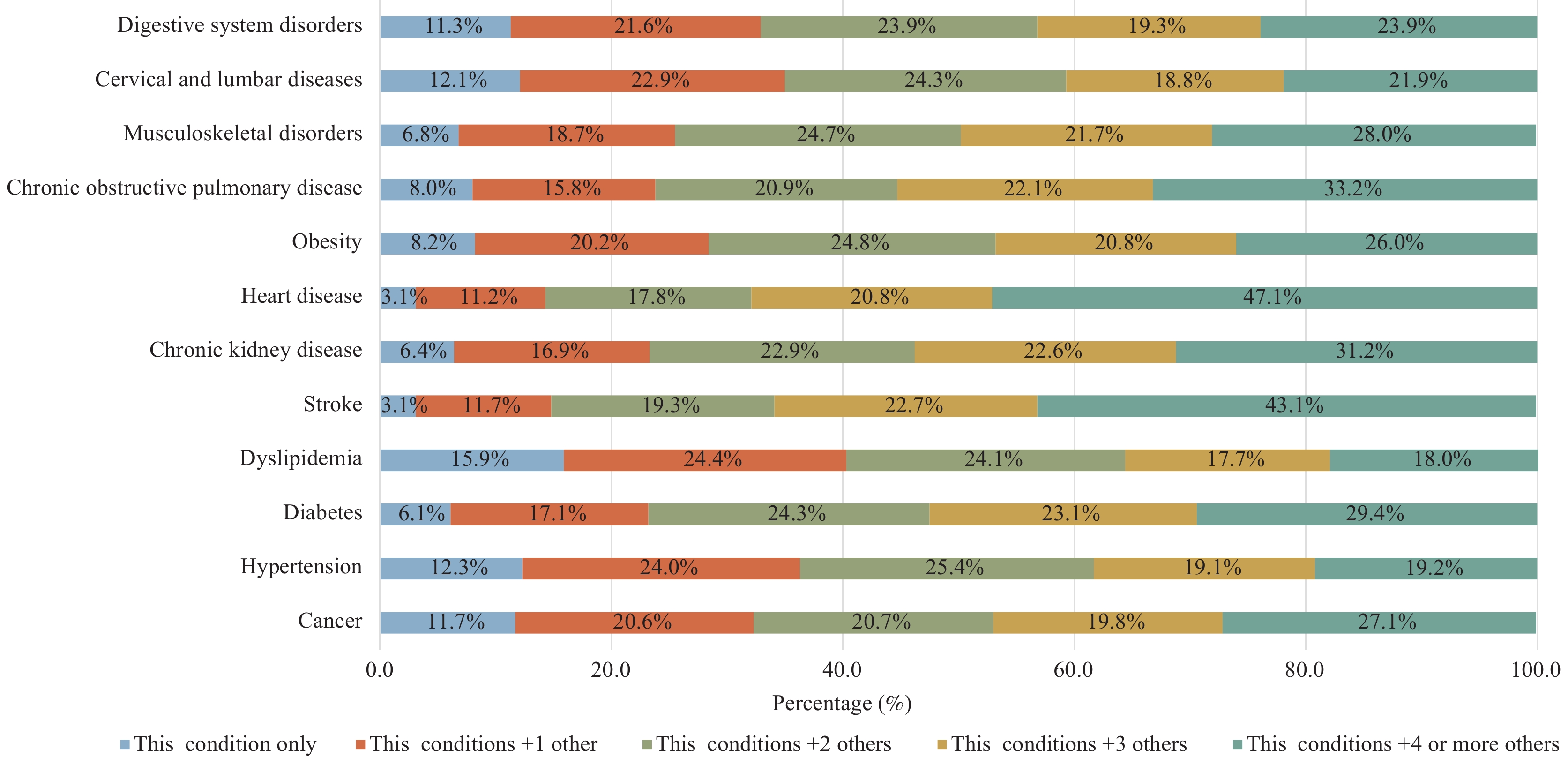
Multimorbidity is becoming more common and poses a major challenge to healthcare systems. However, the prevalence and patterns of multimorbidity among Chinese adults aged ≥18 years are largely unknown.
This study found that 46.5% of Chinese adults had multimorbidity in 2018. And the prevalence of multimorbidity prevalence is increased with age. Prevalence of multimorbidity was higher among men, Han Chinese, adults with lower educational level, and those with lower household income. The most common multimorbidity pattern is a combination of three chronic conditions, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obesity.
As multimorbidity diversifies characteristics and patterns, guideline development, clinical management, and public intervention should consider the complexity of multimorbidity.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed