2023 Vol. 5, No. 10
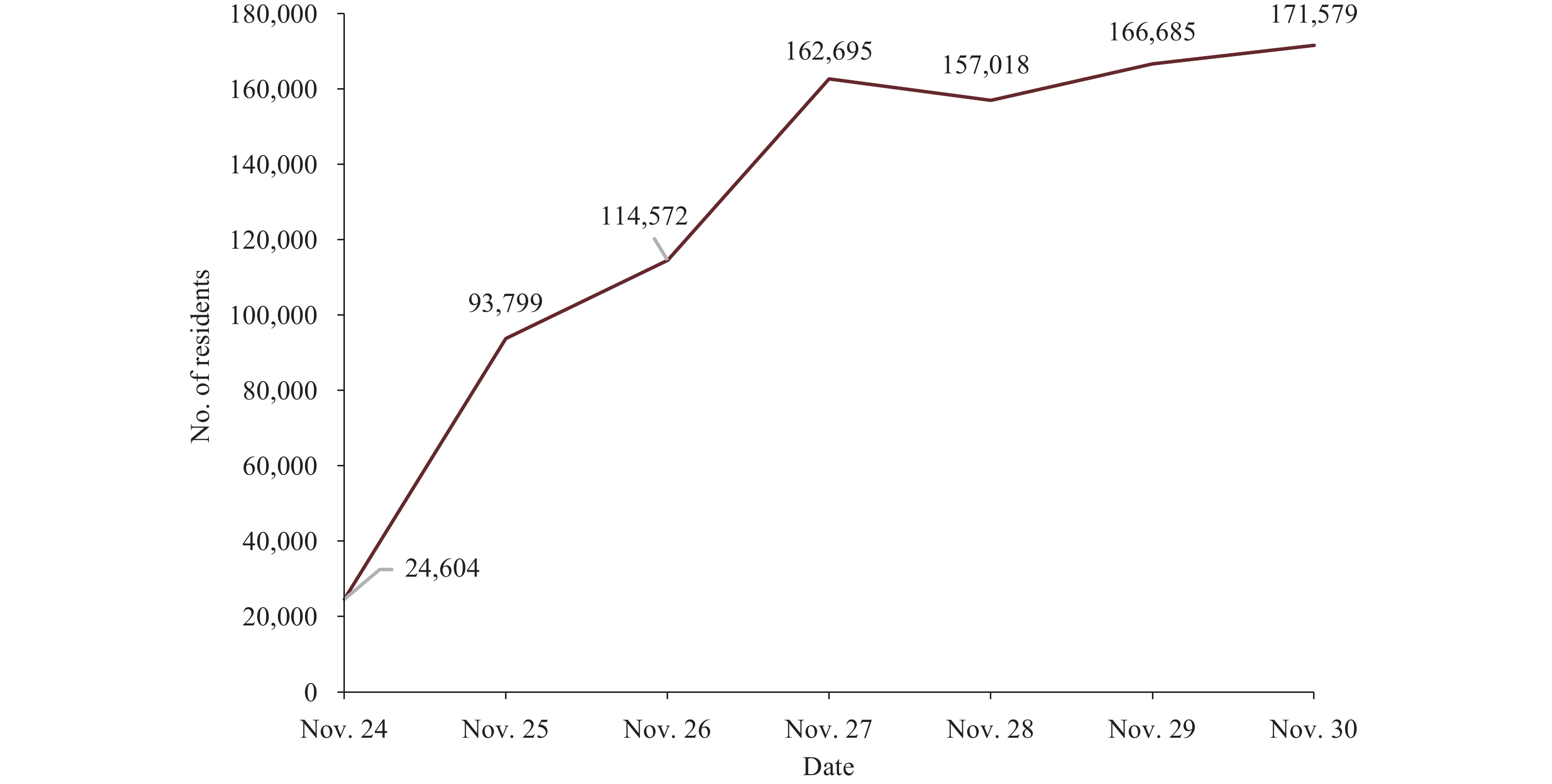
So far, no descriptive analysis has been conducted on community residents with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) nucleic acid self-sampling in China.
This report found that self-sampling had a wide age and regional distribution, with the time from self-sampling to result-reporting typically taking less than one day. Additionally, self-sampling was found to save a considerable amount of manpower and medical resources compared to regular sampling.
The experience of prevention and control measures during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has provided a reference for the prevention and control of other infectious diseases through self-sampling.
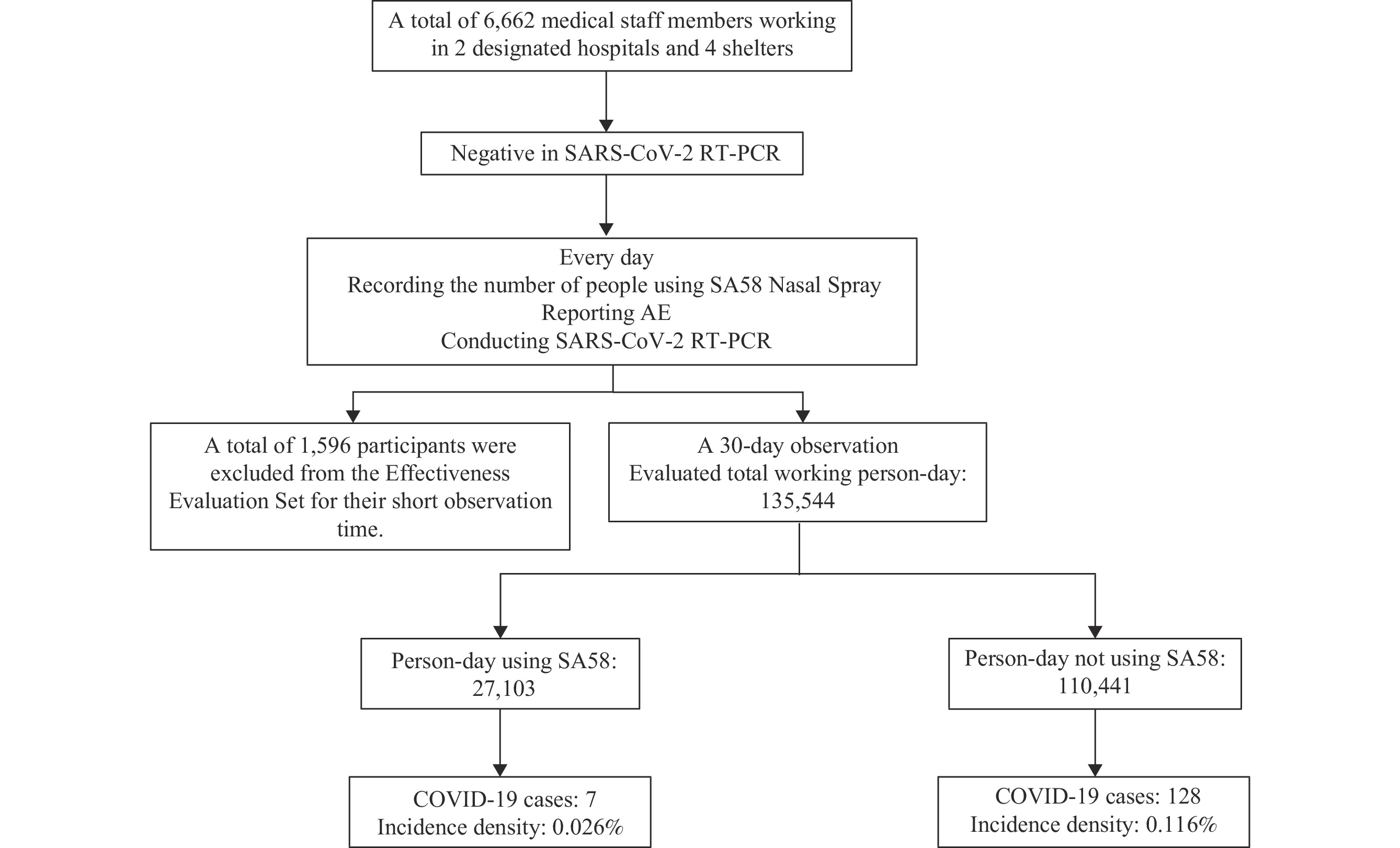
The active ingredient of the SA58 Nasal Spray is a broad-spectrum neutralizing antibody with a high neutralizing capacity against different Omicron sub-variants in vitro studies.
This study demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection in medical personnel for the first time.
This study provides an effective approach for the public to reduce their risk of COVID-19 infection. The findings of this research have the potential to significantly reduce the risk of infection and limit human-to-human transmission in the event of a COVID-19 outbreak.
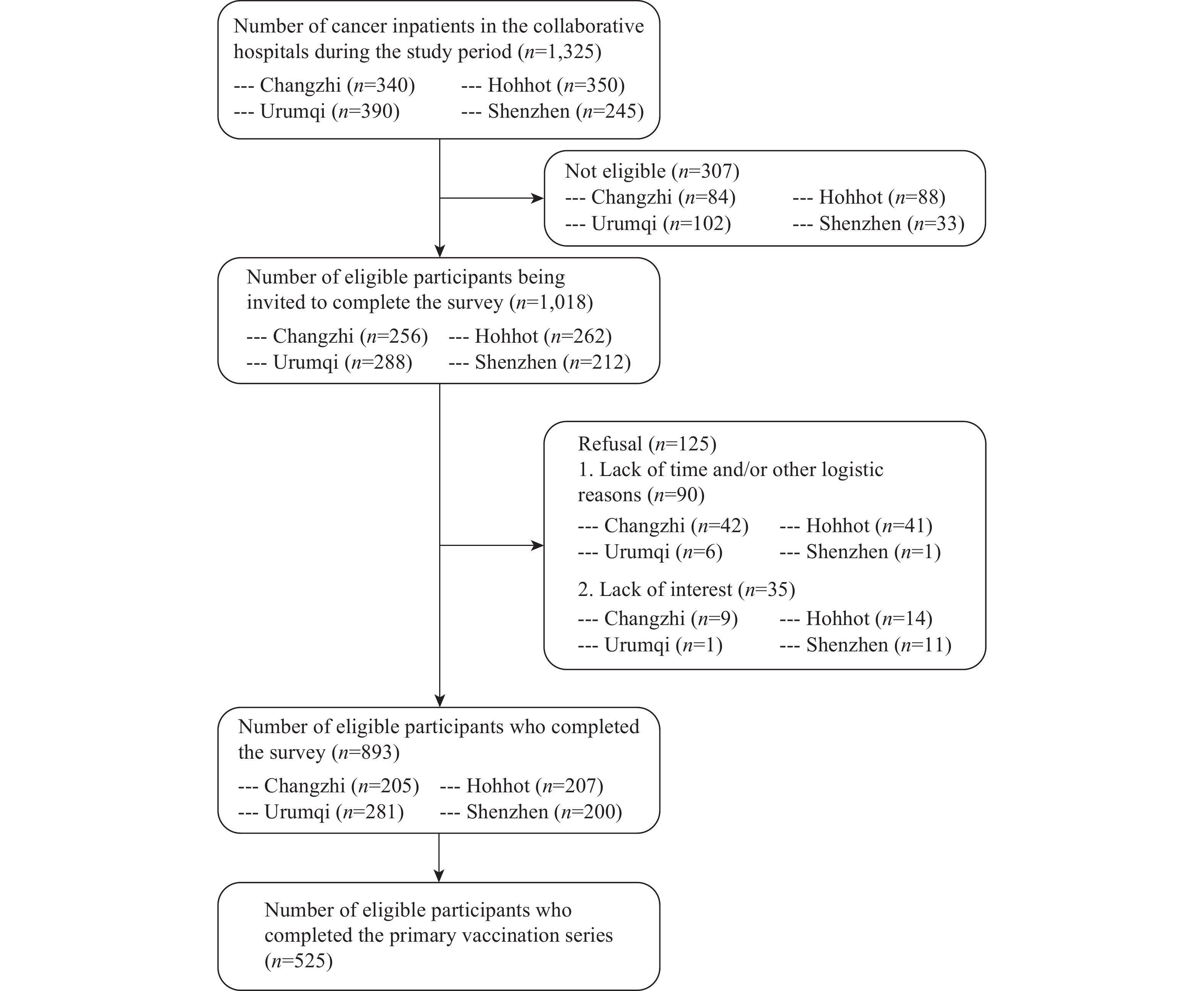
Cancer patients are more vulnerable and have higher mortality rates from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) than the general population; however, coverage for booster doses of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine was low among cancer patients in China.
Overall, 32.0% and 56.4% of cancer patients from four Provincial Level Administrative Divisions (PLADs) expressed hesitancy toward the first and second booster doses, respectively. Factors negatively associated with hesitancy to receive booster doses included positive attitudes, perceived support, and higher exposure to COVID-19 vaccination information. Conversely, postvaccination fatigue was positively associated with vaccine hesitancy.
Improved COVID-19 vaccination coverage is needed to promote health for cancer patients.
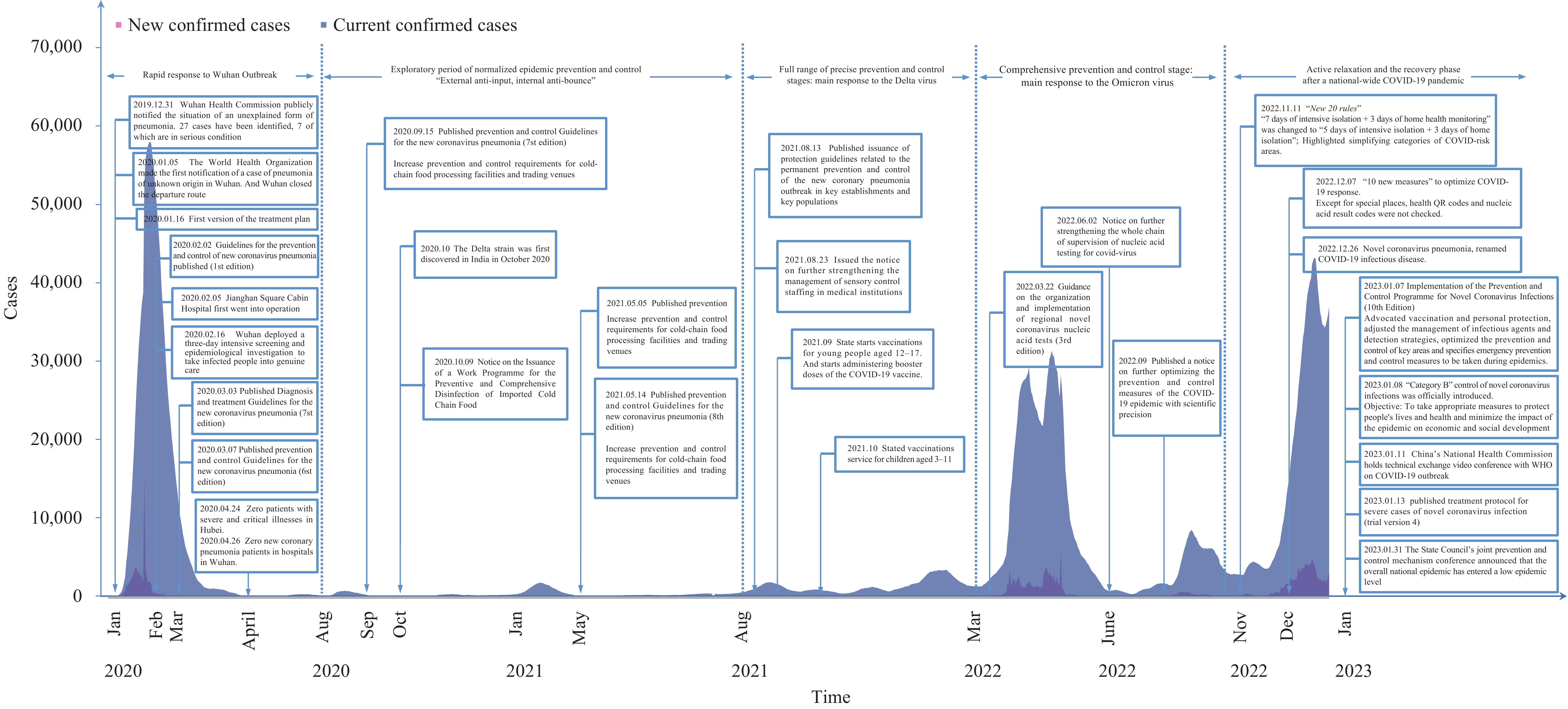
Over the past three years, China has implemented rapid, vigorous, and coordinated control measures to limit the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) effectively. These measures include active containment, graded management, rational resource allocation, rapid contact tracing and disposal, and targeted vaccination of key populations. These efforts have contributed to the prompt and effective control of outbreaks, protecting the health and well-being of older adults. This review provides a comprehensive summary of the changes in China’s COVID-19 prevention and control experiences and other public health measures since the outbreak of the pandemic, and assesses their impact on older adults. It may serve as a valuable reference for future epidemic prevention and control efforts.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed