2022 Vol. 4, No. 32
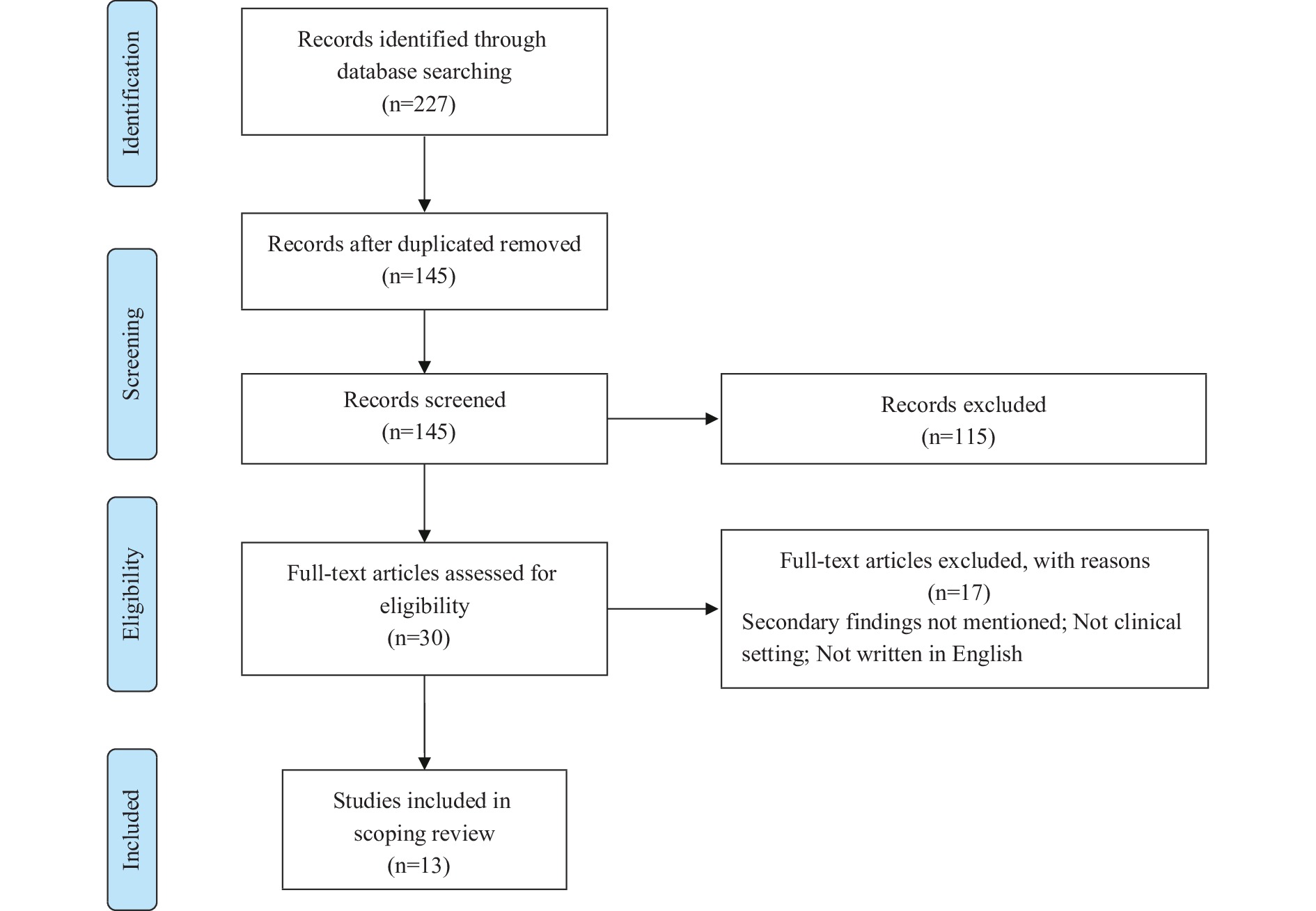
The detection and disclosure of secondary findings (SFs) is a preventive strategy for medically-actionable hereditary health conditions. Some countries have guidelines on management and disclosure of SFs, while others avoid detection and disclosure of SFs. This study is a review of clinical guidelines from six countries and the European Union to identify similarities and differences among SF guidelines. Evidence from this review supports harmonization of guidelines across countries to promote broad international collaborations on genomics and to benefit precision medicine. This study can serve as a reference for development of SF management guidelines in China by contributing evidence from other countries to the ethical and methodological challenges under debate.
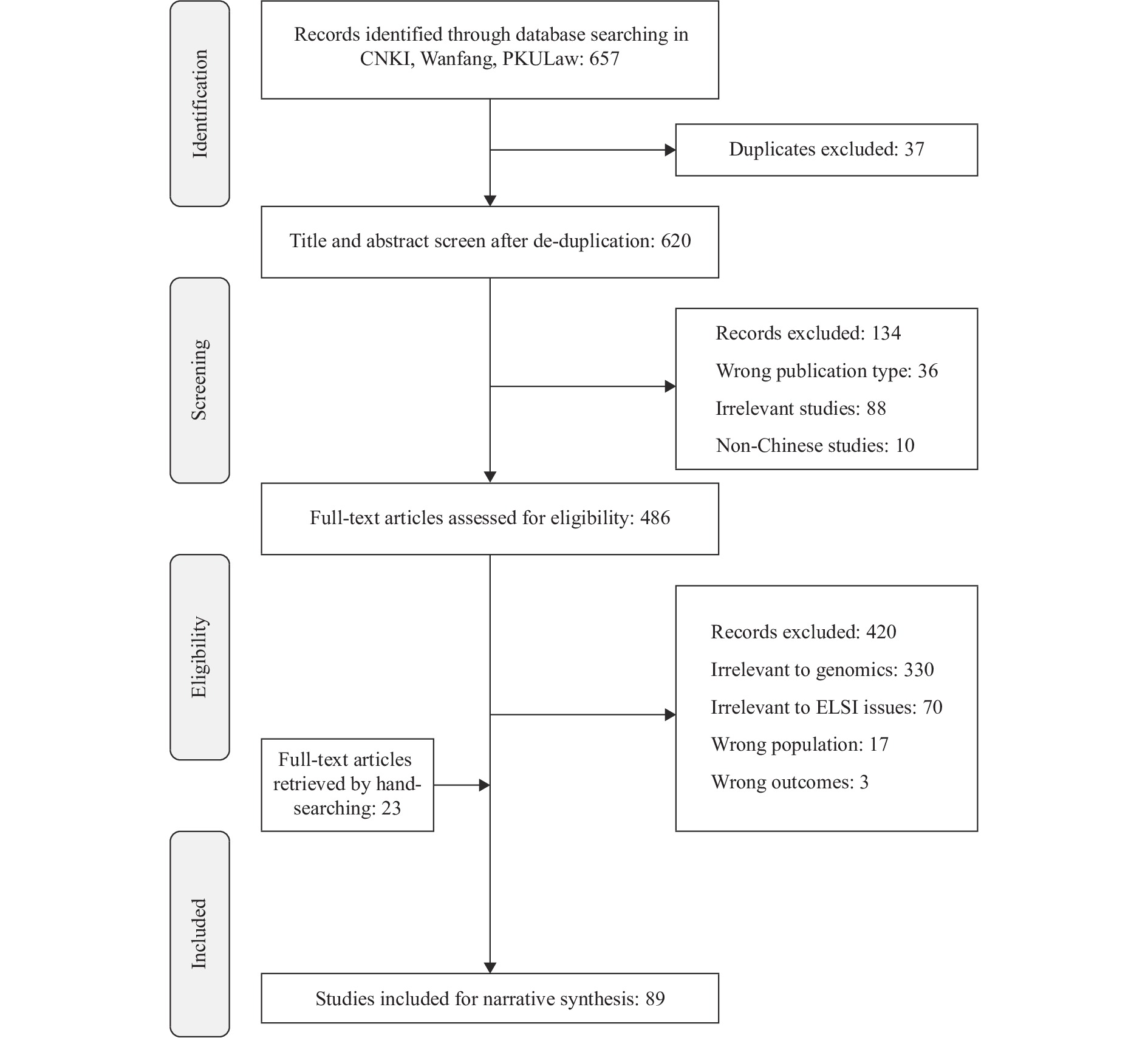
We conducted a scoping review of Chinese language studies on the ethical, legal, and social implications of genomics and identified four broad themes: ethical considerations, regulatory framework, perceptions of genomics and precision medicine, and future directions of genomics. Ethical, legal, and social implications of genomics are growing in importance and are highly relevant to public health in China.
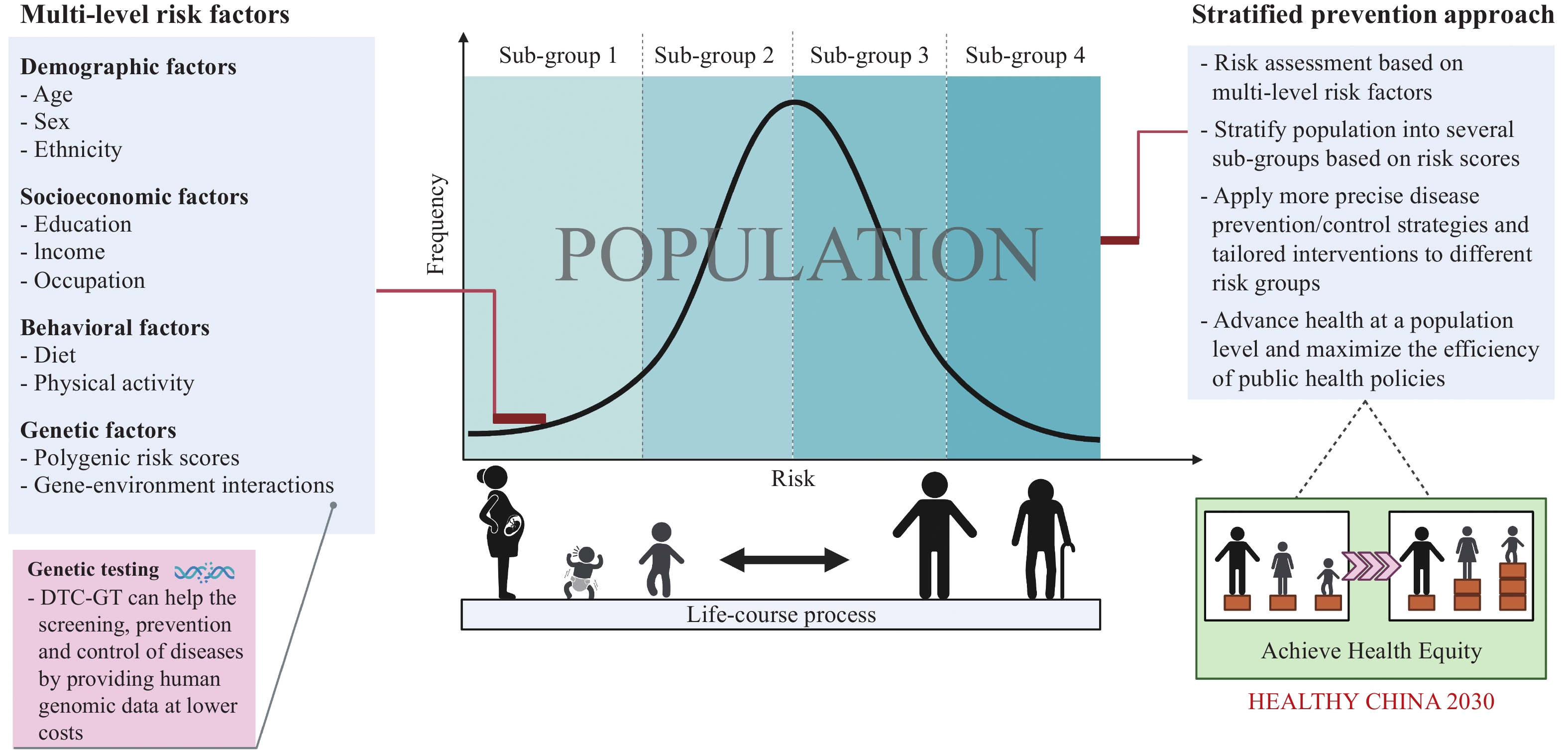
In China, the direct-to-consumer genetic testing (DTC-GT) industry has been undergoing exponential growth during the past few years. This study intends to assess characteristics of DTC-GT users in China, estimate the price elasticity of demand, quantify monetary values of DTC-GT features, and discuss its implications to the development of precision public health.
A total of 629 participants with an average age of 28.8 years were collected from an online survey conducted in November 2021. A discrete choice experiment and a mixed logit modelling approach were used to elucidate consumer preferences to DTC-GT services and evaluate monetary values of certain features.
DTC-GT users were found to have a higher level of income on average. The price elasticity of DTC-GT services was estimated to be −0.72 (95% CI −0.73 to −0.70). The willingness-to-pay to genetic testing features of physical traits, personality, and dietary recommendation were estimated to be 90, 107, and 220 CNY, respectively.
The nature of big genomic data makes DTC-GT have the potential to aid in the advancement of precision public health through more precise disease prevention and control strategies. The study also notes the need for addressing potential drawbacks of DTC-GT and protecting genetic privacy.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed