2021 Vol. 3, No. 6
What is already known about this topic?
Timely screening of high-risk population is important to improve the early detection of brucellosis among the endemic areas during the high incidence seasons, which is also required by the National Brucellosis Prevention and Control Plan (2016–2020) (NBPCP).
What is added by this report?
Seroepidemiological characteristics of brucellosis in high-risk populations were obtained and special occupational populations were found. The seroprevalence of brucellosis has been decreasing compared with that reported in the recent years due to the ongoing implementation of control measures in endemic areas.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Special occupational populations could be promptly detected using routine screening, which makes it possible to initiate standardized treatment for infected patients as early as possible. It also reminds us to pay attention to special occupational populations to improve their knowledge of brucellosis and reduce the risk of infection.
According to the National Brucellosis Prevention and Control Plan (2016–2020) (NBPCP), the awareness rate of high-risk populations in brucellosis-endemic areas should reach 90% by 2020. But the updated results have not been reported.
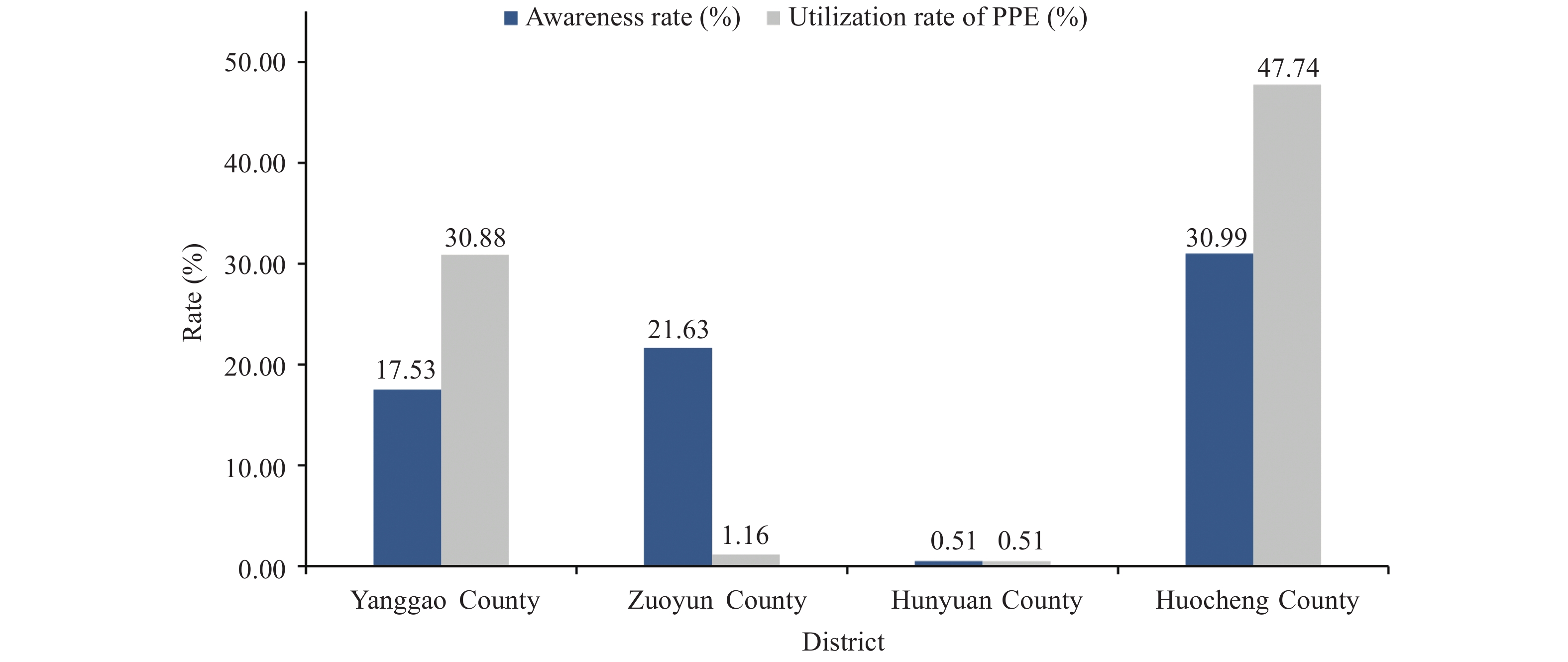
This report determined the awareness rate of brucellosis (17.74%), utilization of personal protective equipment (PPE) (20.13%), and their relationship with seroprevalence, which provides evidence for the effectiveness of the implementation of NBPCP.
The results suggest that health education should be conducted for high-risk populations to improve their brucellosis and protection knowledge.
What is already known about this topic?
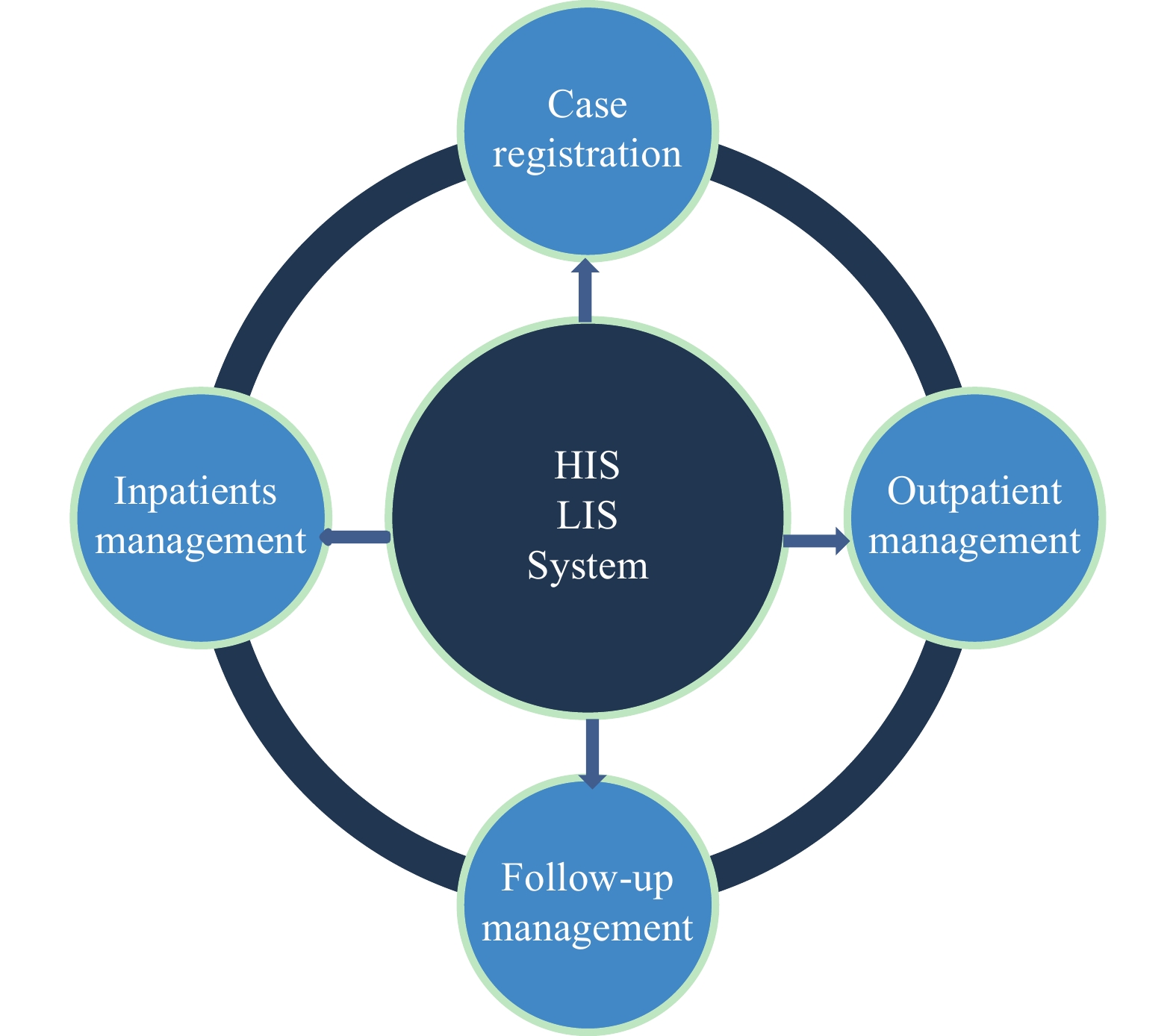
Wulanchabu City Center for Endemic Disease Prevention and Control had established and used a Brucellosis Integrated Information System (BIIS) since 2013. However, it had not been systematically evaluated and promoted so far.
What is added by this report?
The BIIS had significantly improved the efficiency of brucellosis reporting and provided convenience for follow-up management of cases, which was valuable for finishing completely routine therapy. However, the stability of the system needs to be improved.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The results of the BIIS assessment demonstrated its advantages and disadvantages, which could provide some evidence for its implementation in other areas of China.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed