2021 Vol. 3, No. 50
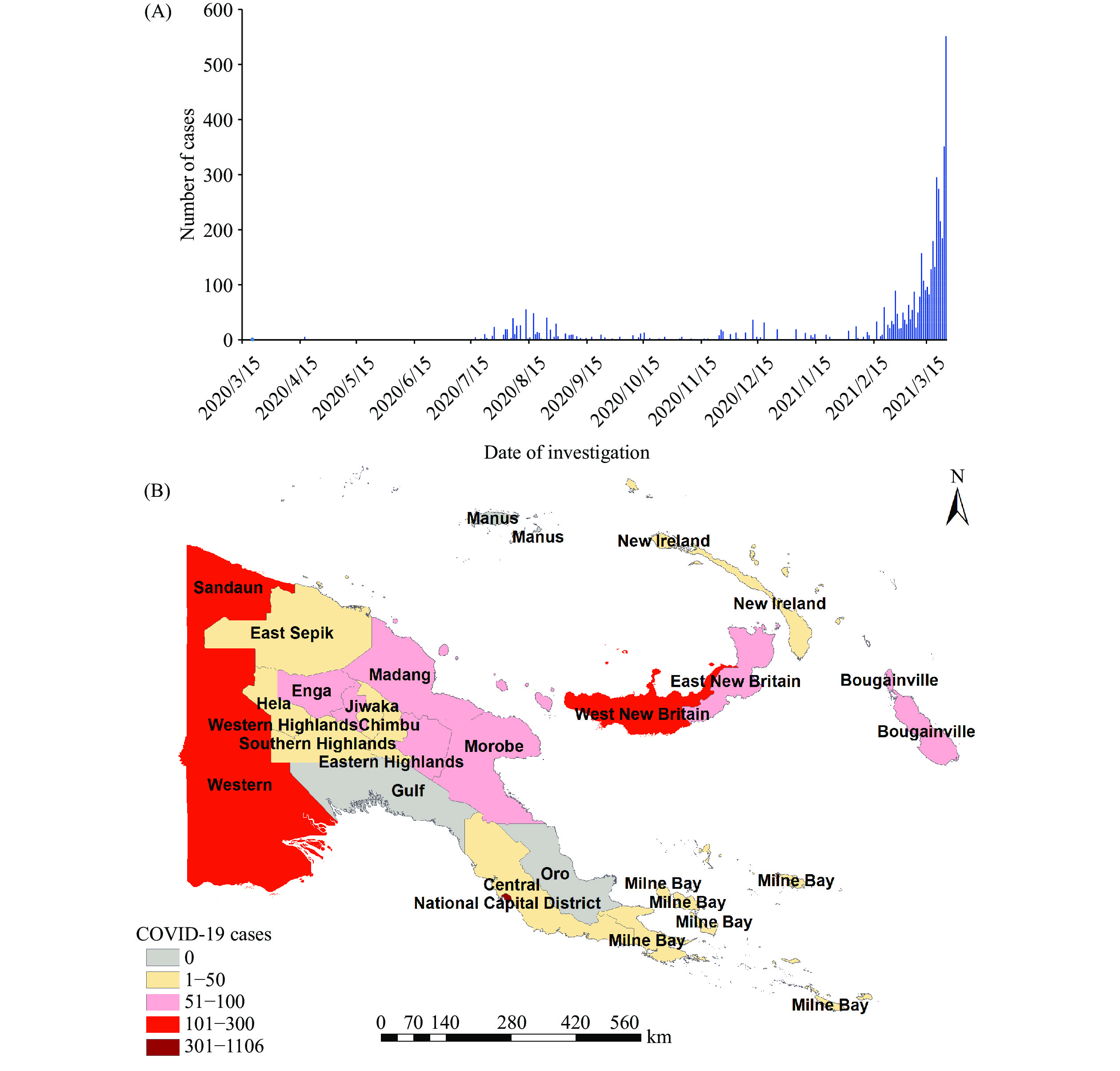
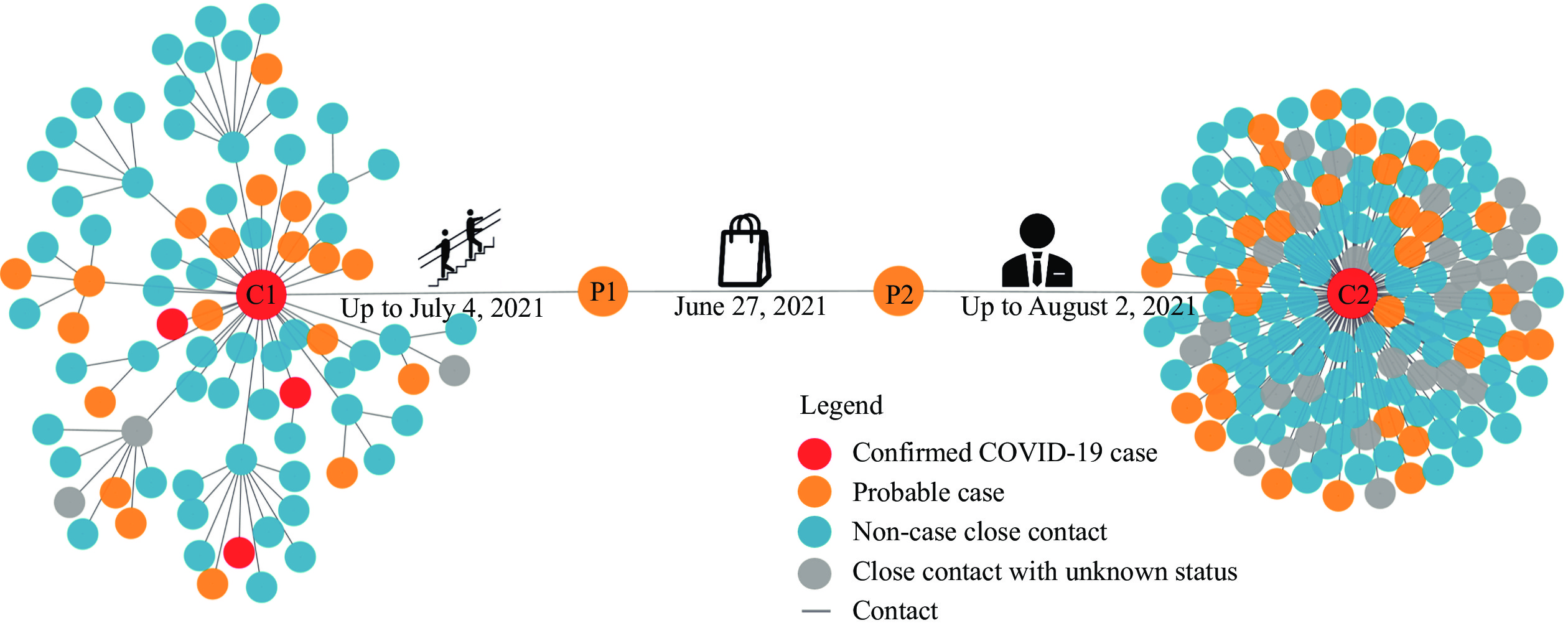
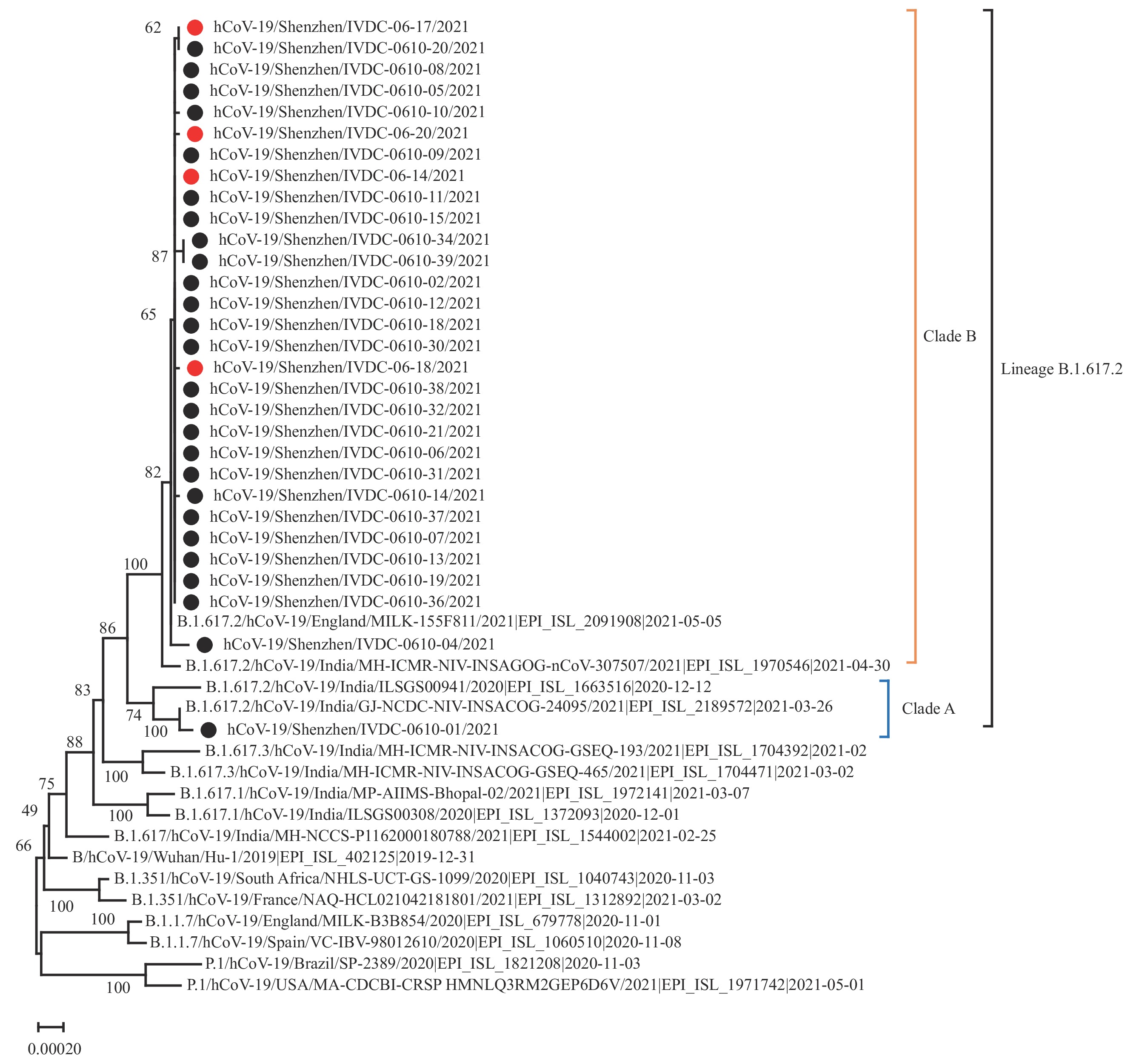
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Delta variant has proved to have increased transmissibility, and mutations that can cause partial immune escape, which makes its transmission more insidious.
This study showed that probable cases who had negative results in nucleic acid testing but had positive IgM test result and/or IgG test value of over 20 S/CO in antibodies testing, might serve as bridges in the Delta variant’s transmission chain.
In border inspection and quarantine, tests for SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibodies should be strengthened alongside nucleic acid tests to prevent probable cases with transmission potential from crossing the land border into China. In contact tracing investigations, the bridging role of probable cases should be considered to reconstruct the transmission chain.
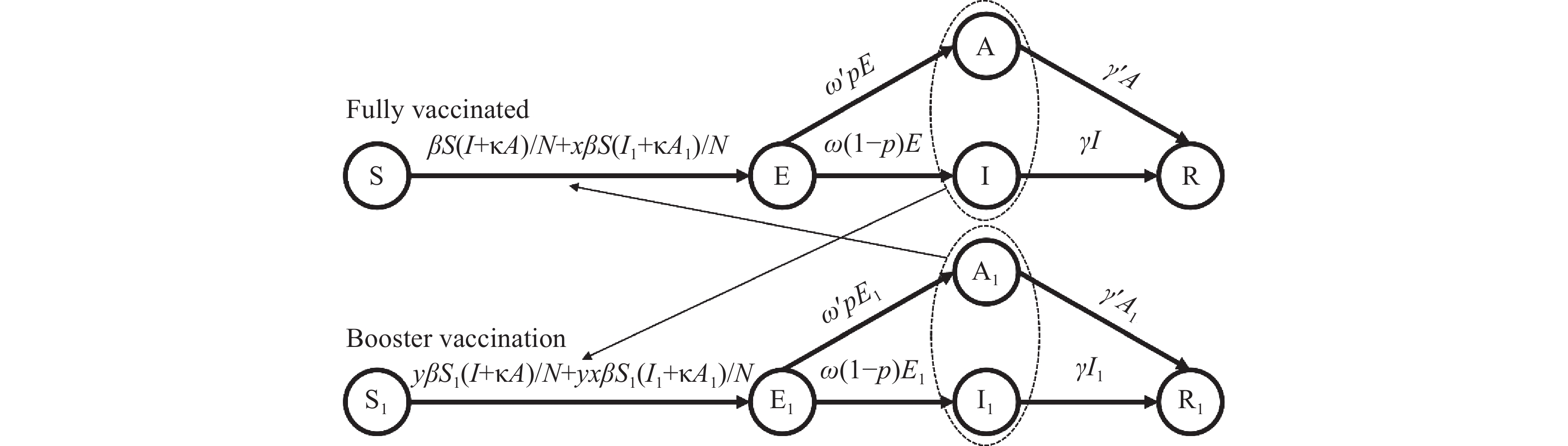
Vaccination booster shots are completely necessary for controlling breakthrough infections of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in China. The study aims to estimate effectiveness of booster vaccines for high-risk populations (HRPs).
A vaccinated Susceptible-Exposed-Symptomatic-Asymptomatic-Recovered/Removed (SEIAR) model was developed to simulate scenarios of effective reproduction number (Reff) from 4 to 6. Total number of infectious and asymptomatic cases were used to evaluated vaccination effectiveness.
Our model showed that we could not prevent outbreaks when covering 80% of HRPs with booster unless Reff=4.0 or the booster vaccine had efficacy against infectivity and susceptibility of more than 90%. The results were consistent when the outcome index was confirmed cases or asymptomatic cases.
An ideal coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) booster vaccination strategy for HRPs would be expected to reach the initial goal to control the transmission of the Delta variant in China. Accordingly, the recommendation for the COVID-19 booster vaccine should be implemented in HRPs who are already vaccinated and could prevent transmission to other groups.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed