2021 Vol. 3, No. 4
What is already known about this topic?
While the establishment of an air quality health index (AQHI) in some countries yielded positive outcomes in communicating health risks of air pollution, China lagged behind in developing its own AQHI. Several research studies of AQHI were conducted in China, but this scientific research has not yet been applied to standards.
What is added by this report?
This report introduced the method of calculation of Chinese AQHI to be launched in pilot cities. The index in this report was established on the basis of fully drawing on international experience and considering Chinese characteristics.
What are the implications for public health practice?
The purpose of this report is to guide unified application of the AQHI throughout China and translate scientific evidence into public services to promote public health. Based on the AQHI construction method in this report, an AQHI real-time computing platform and data transfer interface will be developed. The release of AQHI aims to communicate health risk of air pollution and provide scientific health protective guidance to the general public, accordingly to protect people’s health.
The incidence of falls among older people is 20.7% in China. Falls are the top cause for death from injuries in people aged 65 years and above, and mortality rates increase with age in China. There are few reports on the epidemiological characteristics of falls in older people nationwide in recent years.
This study found that among older people with falls reported in the National Injury Surveillance System (NISS) in 2018, there were more females than males. The peak time for falls was in the morning. Home was the most common site where falls occurred, and leisure activities and housework were the main activities when falls occurred. After falling, the lower limbs and head were most often injured with bruises and fractures. The degree of injury was mainly mild and moderate.
Data based on the NISS can be used as an additional data source for research on falls in China. This study identified priorities for the control and prevention of falls.
What is already known on this topic?
Healthy aging among Chinese older people has low prevalence. Some sociodemographic and lifestyle factors were shown to be associated with healthy aging.
What is added by this report?
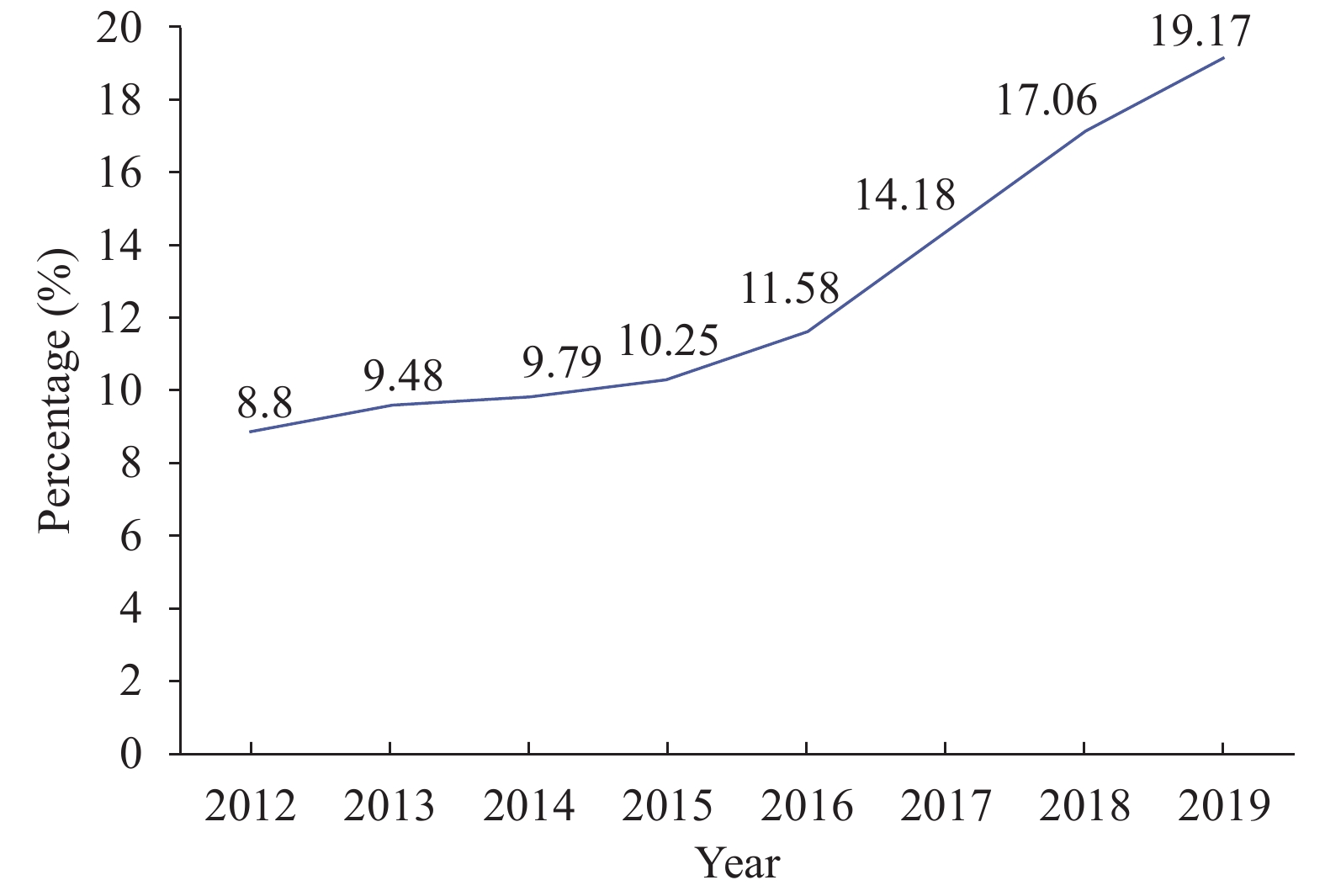
The age-adjusted prevalence of healthy aging in the 6 provincial-level administrative divisions (PLADs) of China is 15.8 % in 2019. County-level factors, such as the prevalence of healthy communities in a county, as well as some sociodemographic variables and physical exercise, are potential factors of healthy aging.
What are the implications for public health practice?
These findings showed that more targeted actions, including generalizing healthy communities and individual-level interventions, may be of great importance for healthy aging.
As the first of 15 Healthy China initiatives, the Health Education Initiative has the crucially important goal of improving citizens’ health literacy. There are two key activities in the initiative for improving health literacy. The first is to establish a mechanism for dissemination of health sciences knowledge through development of national and provincial databases of health sciences expertise and a national resource of accessible health knowledge. The second is to establish a health education and health promotion performance evaluation mechanism for medical institutions and medical personnel. In this paper, we analyzed the content and strategies of these two health educational activities.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed