2021 Vol. 3, No. 35
Morbidity and prevalence of several major parasitic diseases have been declining in China. To reduce the disease burden of parasitic diseases and protect public health security, conducting accurate diagnoses following timely treatment is important.
In the national competition held in 2019, the overall accuracy rates of participants for theoretical knowledge and slides interpretation for parasitic diseases were 80.44% and 66.87%, respectively. Significant differences in the accuracy rates of detecting schistosomiasis or malaria existed between endemic areas and non-endemic areas, respectively.
The study results will help policymakers and health managers to identify the gaps in parasitic diseases, help to strengthen diagnostic capacity, and improve quality of control programs.
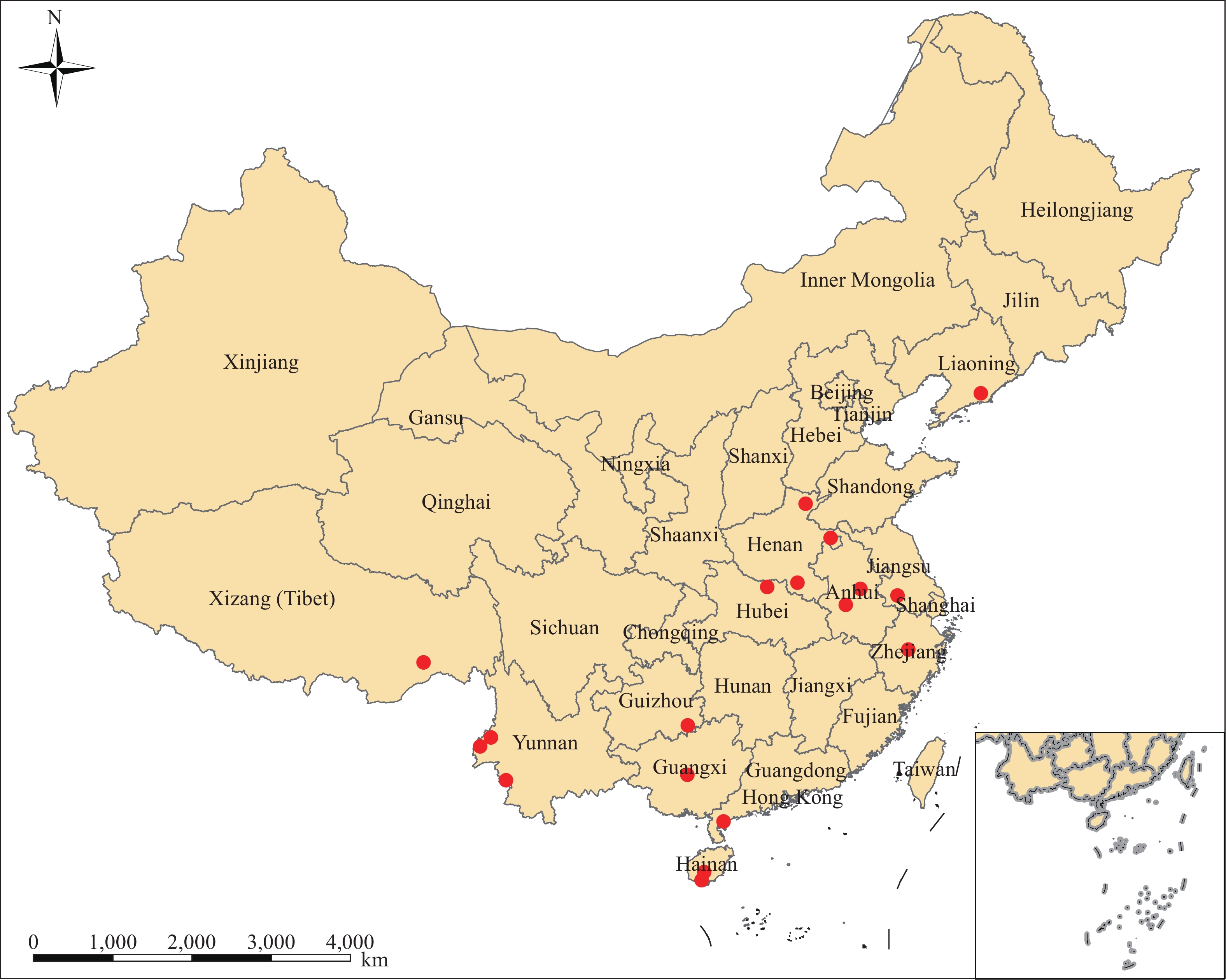
Triatoma rubrofasciata is a potential vector that can transmit American trypanosomiasis and was widely recorded in South of China.
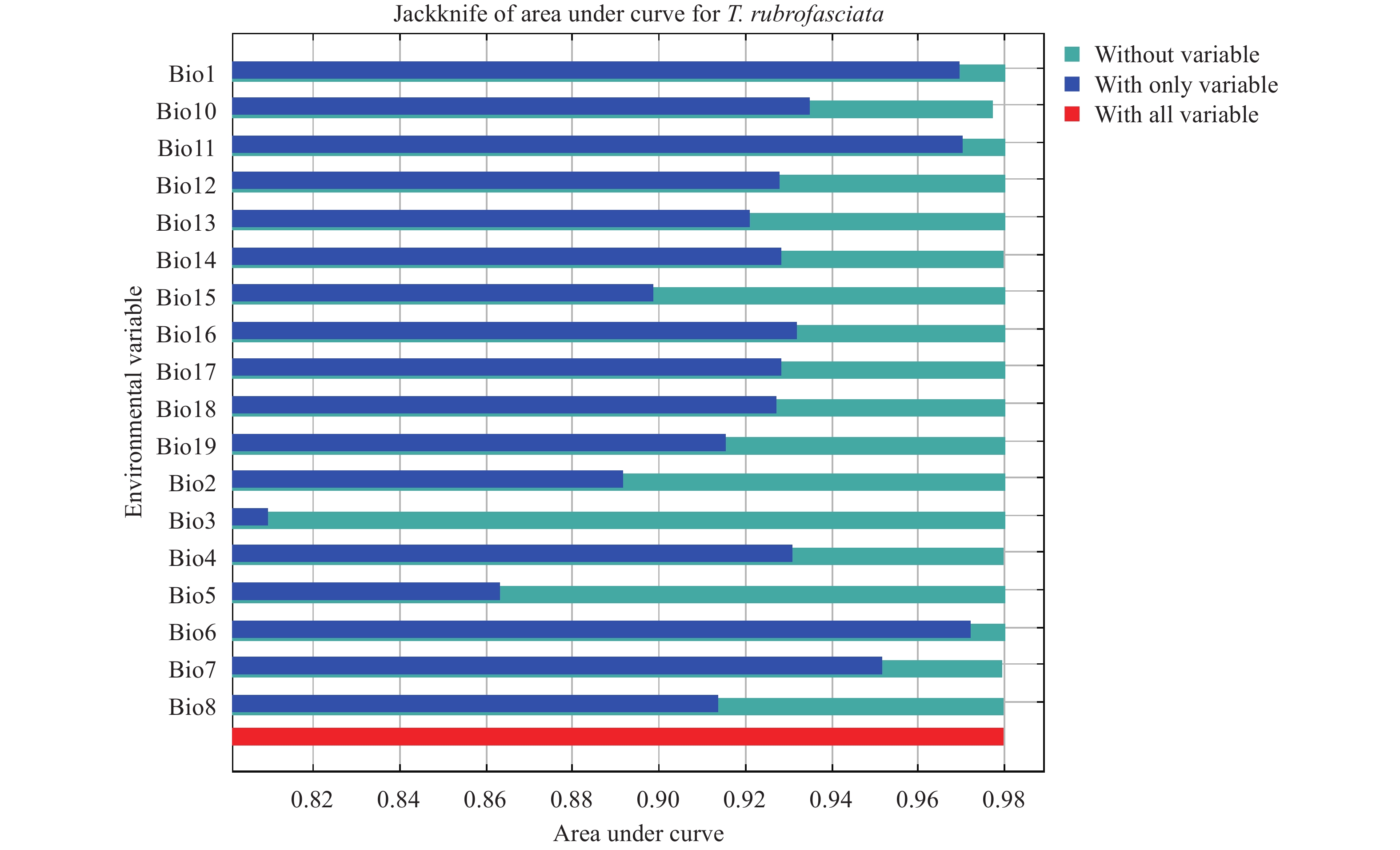
Because of the low density of the triatomines, more habitats have not been discovered. This study mainly focused on predicting the geographical distribution of T. rubrofasciata under current and future climatic conditions in China using the MaxEnt model.
The result showed that the distribution of T. rubrofasciata was largely affected by annual mean temperature and possessed a high potential for expansion in southern China in the future. Our predictions are useful for targeting surveillance efforts in high-risk areas and increasing the efficiency and accuracy of public health investigations and vector control efforts in China.
Malaria is an infectious parasitic disease transmitted by the bite of Anopheles mosquitoes and is a serious threat to human health. Surveillance of malaria vectors is part of the integrated strategy for malaria elimination in China.
This research supplements the population distribution, density, and seasonal fluctuation of malaria vectors in the Anopheles surveillance sites from 2018 to 2020 in China.
Continuous surveillance of malaria vectors is important for maintaining malaria-free status in China and for providing a scientific basis for risk assessment of malaria retransmission.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed