2021 Vol. 3, No. 32
What is already known about this topic?
Dramatic heatwaves frequently occurred simultaneously with the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic worldwide in 2020 and posed public health challenges. Public risk perceptions and behavioral responses to this compound risk need to be addressed.
What is added by this report?
During heatwaves, the proportion of individuals who perceived COVID-19 to be more concerning than heatwaves decreased by 9.4%, and the behavior of continuously wearing masks reduced by 20.6%. Heatwave exposures also corresponded to an average decline of 58% in the likelihood of continuously wearing masks and a decline of 41% in taking well-ventilated public transportation.
What are the implications for public health practice?
At-risk populations should be effectively prepared to respond to compounded risks from heatwaves occurring at the same time as COVID-19 outbreaks to better address threats caused by climate change.
What is already known about this topic?
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic in China had been effectively controlled for several months, but as the ambient temperature dropped, large gathering-initiated epidemics occurred in northern China, including Hebei, Liaoning, and Jilin provinces.
What is added by this report?
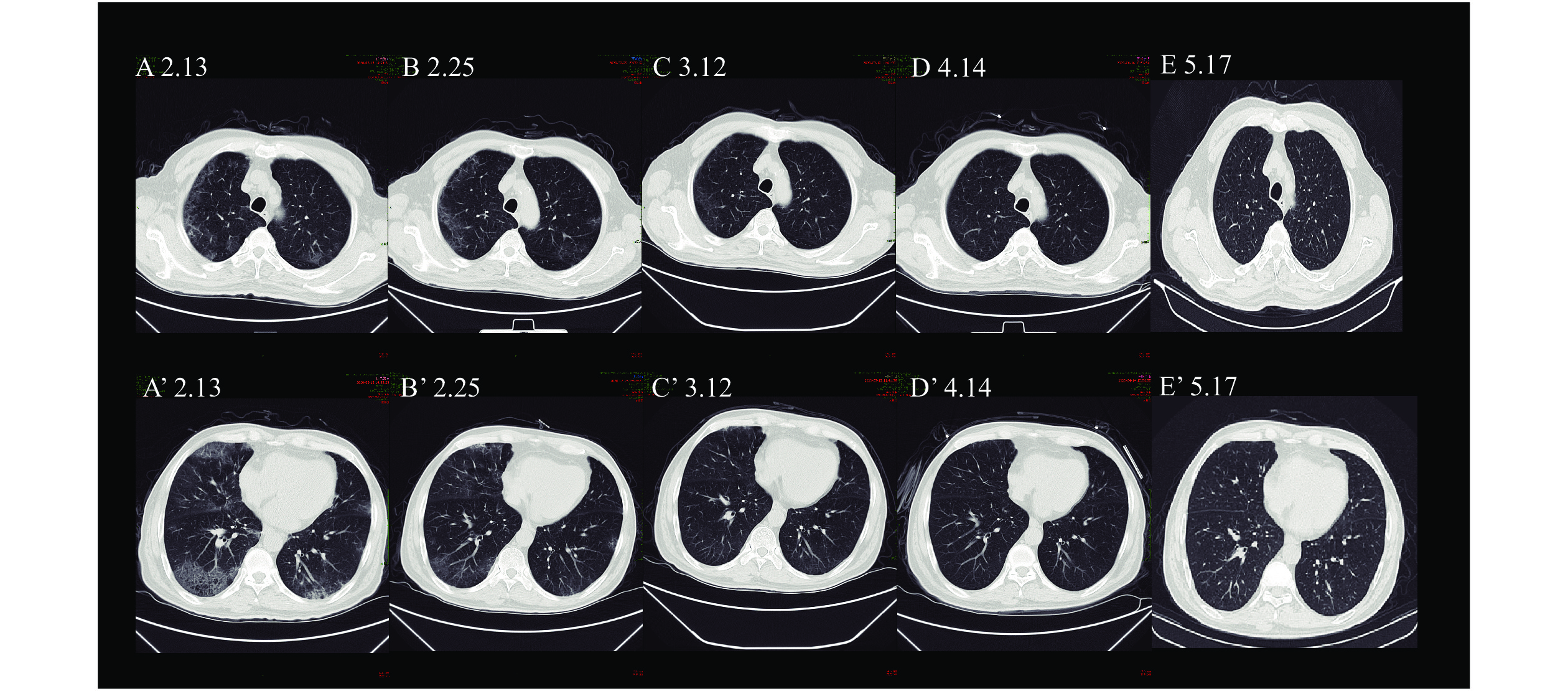
A sudden epidemic emerged in Wangkui County, Suihua City, Heilongjiang Province, on January 9, 2021. An asymptomatically-infected resident of Harbin City returned from Suihua and triggered a large-scale outbreak in the Zhengda Food Processing Company in Harbin, Heilongjiang. The epidemic was associated with widespread community transmission inside and outside the company, eventually leading to 260 persons being infected (87.8% of 296 patients in Harbin).
What are the implications for public health practice?
This study demonstrates the importance of screening for infections in the COVID-19 prevention and control system, shares experiences identifying and managing asymptomatic infections, and recommends food processing enterprises like the Zhengda Company to improve preventative measures. Our evidence-based epidemiological analyses provide methods for finding high-risk settings and evaluating epidemic situations when many asymptomatic patients are identified in a short period of time.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed