2021 Vol. 3, No. 31
What is already known on this topic?
High-level intakes of both cooking oil and salt are issues of concern in China as they can lead to an increased risk of chronic diseases later in life. Reducing intakes of cooking oil and salt should be prioritized in children.
What is added by this report?
Among children aged 6–17 years in China in 2016–2017, the median intake of cooking oil and salt were 27.7 and 6.1 g/d, respectively. The percentages of children with intake of cooking oil and salt that exceeded the recommended guidelines were 50.4% and 67.8%, respectively.
What are the implications for public health practice?
Understanding the consumption levels of cooking oil and salt among children aged 6–17 years in China is vital for reducing associated health effects later in life. This study provided scientific evidence to recommend policymakers formulate effective policies to reduce intake of cooking oil and salt for the target population.
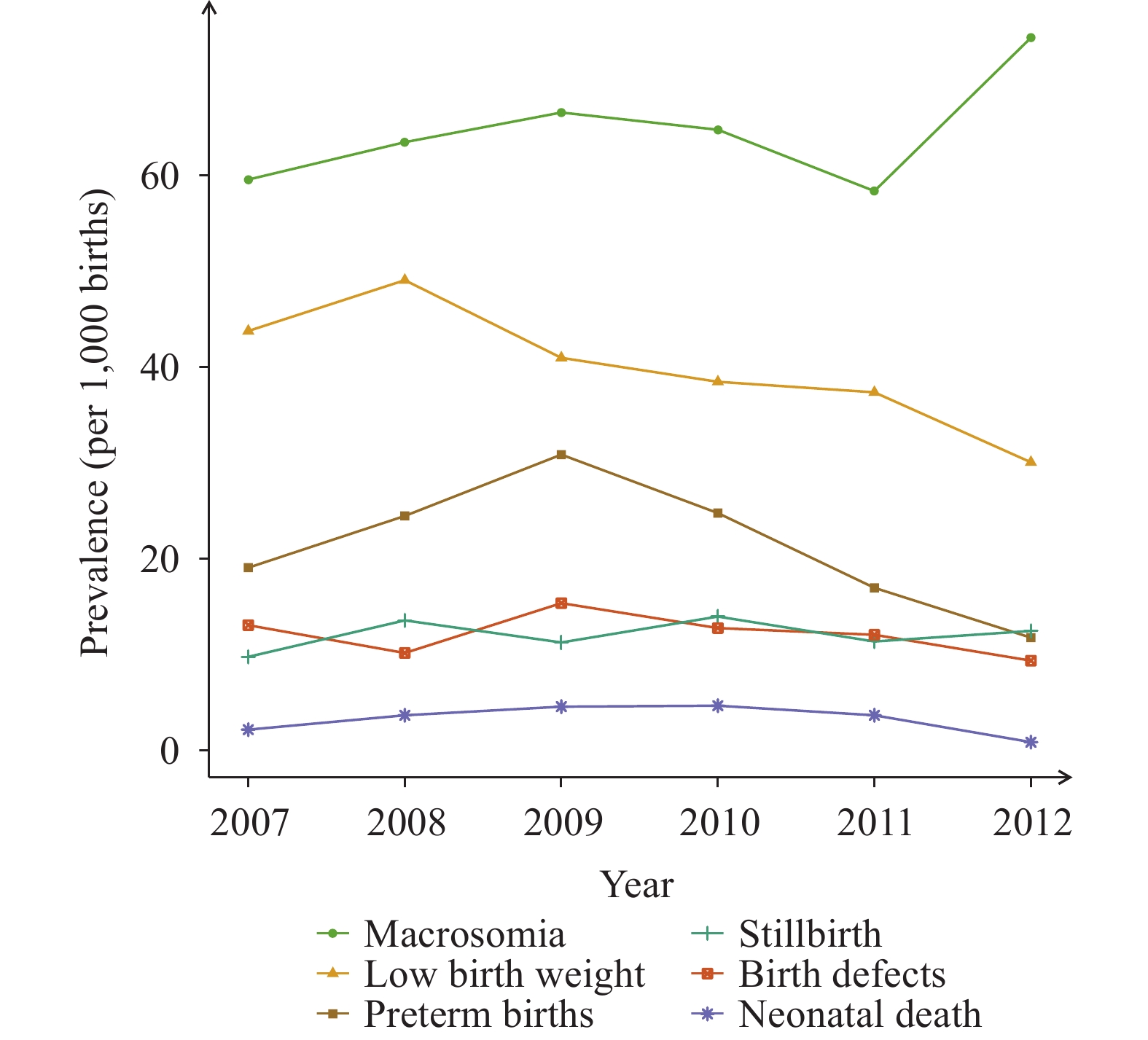
What is already known about this topic?
Shanxi Province in northern China has been identified as a region with the highest prevalence of birth defects nationwide. With large amounts of financial support devoted for prevention and related interventions for birth defects, huge progress has been made as a 60% decrease in its prevalence was observed from 2009 to 2014.
What is added by this report?
The study presented a recent trend of adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs) in Shanxi Province, a region with high prevalence of birth defects in China from 2007–2019. The prevalence of serious APOs including birth defects, stillbirths, and neonatal deaths remained at a relatively low level, yet macrosomia, low birth weight (LBW), preterm births, and spontaneous abortion comprised a majority of all APOs, with macrosomia showing an obvious upward trend from 2007 to 2012.
What are the implications for public health practice?
These findings provide new evidence for prevention and intervention strategies of APOs in northern China. Future research should focus on comprehensive interventions for multiple APOs, especially macrosomia, LBW, preterm births, and spontaneous abortion.
Introduction: This study analyzed views and downloads of articles published in China CDC Weekly from 2019 to 2020 as part of an evaluation of the academic level and quality of the journal.
Methods: The study included articles published between November 29, 2019 and December 25, 2020 and evaluated views and downloads through February 9, 2021 using standard bibliometrics. We conducted network analysis with VOSviewer software.
Results: There were 283 articles from 101 institutions published in China CDC Weekly during the analysis period, among which 22 (21.8%) institutions were overseas institutions. There were 220 unique first authors, with 1.28 articles per first author. There were 2,404,882 views and 58,760 downloads in total. The article with the highest view and download counts had 1,244,826 views and 38,978 downloads. Article types with more than 4,500 views per article were Vital Surveillance, Notes from the Field, and Preplanned Studies. Subjects with more than 3,500 views per article were epidemiology of infectious diseases, epidemiology of non-infectious diseases, and maternal and child health. Articles with descriptive research and articles discussing public health monitoring received more attention, shown by larger average per article page views.
Discussion: Study results can help the editorial department improve the journal’s international influence through targeted measures, such as adjusting article types according to view and download analyses and increasing the proportion of international manuscripts selected.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed