2020 Vol. 2, No. 48
An estimated 1,400 new cases of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) occur every day among youths globally. However, HIV distribution among youth aged 15–24 years in China has not been researched extensively.
Between 2010 and 2019, a total of 141,557 HIV cases among the group aged 15–24 years were reported in China with a male to female ratio at 4.07∶1. The main route of HIV transmission was unprotected sex among men who have sex with men (MSM), and heterosexual transmission for females.
Effective HIV control and prevention measures need to target youth aged 15–24 years, especially among MSM. Sexual health education and HIV prevention should start from primary and secondary school levels.
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) had been proved to be effective in HIV prevention among men who have sex with men (MSM) internationally. Use of either PrEP or PEP was found to be limited among Chinese MSM. Relatively little data was reported in China.
Our program indicated that PEP was more acceptable than PrEP among MSM in China. Drugs of lower cost and related knowledge dissemination could increase PrEP and PEP uptake among MSM in China.
PrEP and PEP are likely to contribute significantly to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) prevention in China.
What is already known about this topic?
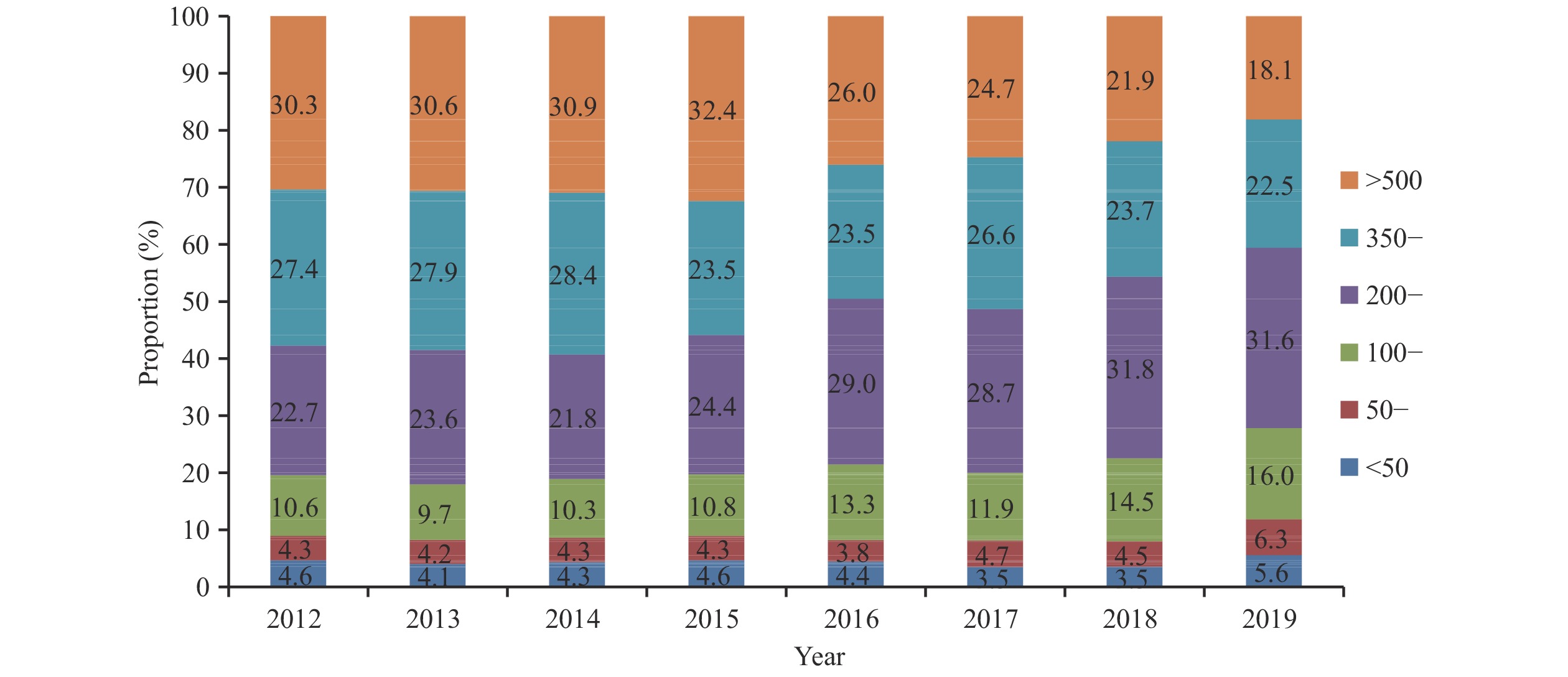
The annual rates of newly diagnosed cases of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are increasing in China, yet the annual number of newly diagnosed cases of HIV infected through injection drug use (IDU) is decreasing.
What is added by this report?
Newly diagnosed cases of HIV infected through IDU in China from 2012 to 2019 show decreases year over year, but the risk of new infections through injecting drugs still exists.
What are the implications for public health practice?
This study highlighted that new HIV infections through IDU continue to be at a low level. However, individuals that are newly diagnosed as HIV-positive through IDU need to have their baseline CD4 T+ lymphocytes (CD4) cell counts monitored and have their sources of infections traced.



 Subscribe for E-mail Alerts
Subscribe for E-mail Alerts CCDC Weekly RSS Feed
CCDC Weekly RSS Feed